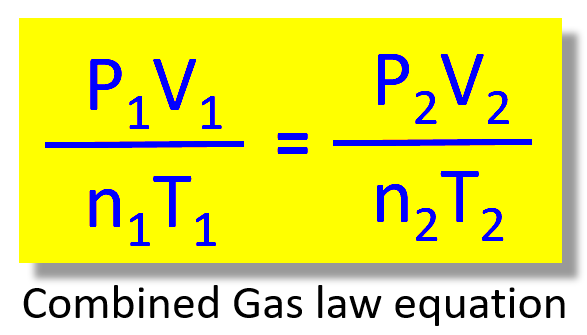Understanding the Combined Gas Law with This Simplified Guide
When I came across the Combined Gas Law in my chemistry lessons it felt like a daunting puzzle of formulas and factors. However similar to a recipe breaking it down into components reveals its logic. The Combined Gas Law merges Boyle’s Law, Charles’s Law and Gay Lussacs Law into a unified equation demonstrating the interplay between pressure, volume and temperature in gases. It’s akin to grasping how various ingredients in a dish influence one another to achieve a harmonious taste. Lets explore the significance of this law and how it streamlines gas law computations.
Breaking Down the Key Components
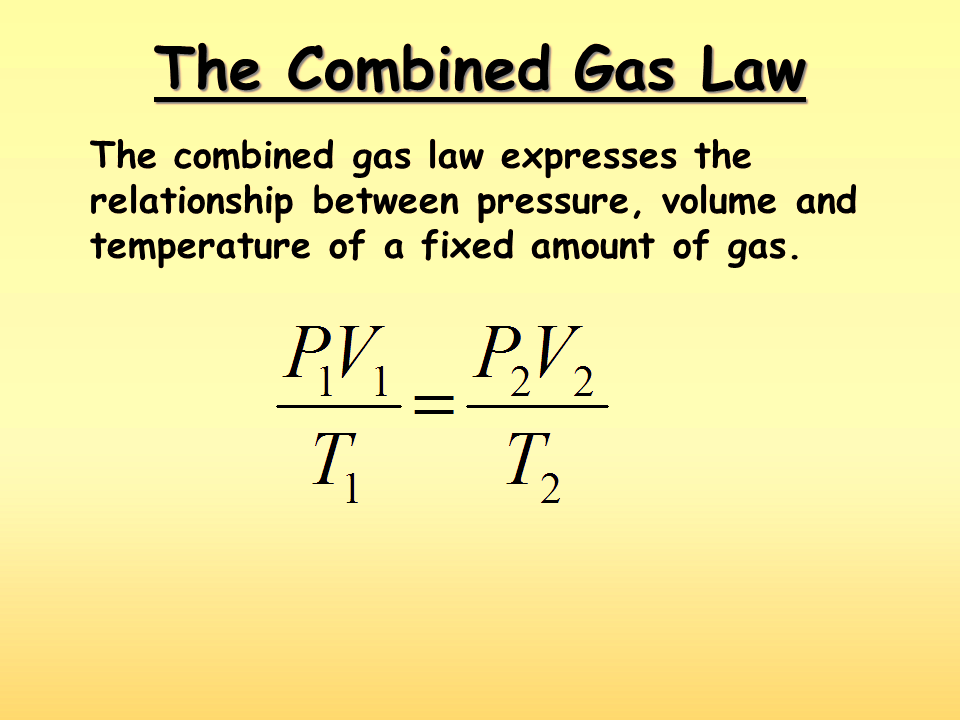
To really understand the Combined Gas Law, we should break down its parts. This law brings together three key gas laws.
- Boyle’s Law: States that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume when temperature is constant. Imagine squeezing a balloon—the more you squeeze, the higher the pressure inside.
- Charles’s Law: Explains that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is constant. Think of a hot air balloon; as the air inside warms up, the balloon expands.
- Gay-Lussac’s Law: Indicates that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when volume is constant. Picture a can of aerosol being heated; the pressure inside increases as the temperature rises.
The Combined Gas Law formula is:
| Formula | Description |
|---|---|
| P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 | Where P is pressure, V is volume, and T is temperature. Subscripts 1 and 2 denote the initial and final states of the gas. |
By grasping the intricacies of each element, one can gain a better hold on the bigger picture, making it easier to tackle challenges.
How the Combined Gas Law Applies to Real-World Scenarios
Observing the Combined Gas Law in practice can be really insightful. Lets consider a real life scenario involving a gas cylinder used for welding. Picture the cylinder at room temperature with a specific pressure and volume. When the cylinder gets heated during use the gas inside expands. This is where the law comes into play;
- Before Heating: Suppose the cylinder has a pressure of 10 atmospheres, a volume of 5 liters, and a temperature of 300K.
- After Heating: If the temperature rises to 350K, the Combined Gas Law helps predict the new pressure or volume, ensuring safety and efficiency.
Based on my personal observations I’ve come to appreciate the significance of this law in laboratory environments where maintaining conditions is vital. Utilizing the Combined Gas Law allows you to predict how gases will react under varying circumstances, which can be beneficial in areas ranging from manufacturing procedures to research studies. It serves as a finely calibrated compass, navigating the intricacies of gas behavior.
Examples to Illustrate the Combined Gas Law
To grasp the concept of the Combined Gas Law better, real life examples can be helpful. Lets take a common situation that most of us can relate to using a bicycle pump. Picture this you’re filling up a tire. When you push down on the pump handle you’re reducing the space inside the pump which causes the air pressure to rise. This is where the Combined Gas Law comes into play:
- Initial Conditions: Suppose the initial pressure inside the pump is 1 atmosphere, the volume is 2 liters, and the temperature is 300K.
- After Pumping: You compress the pump, decreasing the volume to 1 liter. The temperature might rise slightly due to the work done. The Combined Gas Law helps you calculate the new pressure.
Let’s use the formula:
| Initial Pressure (P1) | Initial Volume (V1) | Initial Temperature (T1) | Final Volume (V2) | Final Temperature (T2) | Final Pressure (P2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 atm | 2 L | 300 K | 1 L | 320 K | ? |
Using the Combined Gas Law you can see a notable increase in the final pressure P2. This scenario demonstrates how altering one factor influences the others providing valuable insights for real world situations.
Common Misconceptions and Pitfalls
Grasping the Combined Gas Law can be challenging, with several misconceptions cropping up. A common mistake is mixing up the variables of the law and how they relate to each other. Let’s clarify some of these confusions.
- Misconception: “The law only applies to ideal gases.” While the law is based on the ideal gas model, it can also approximate real gases under many conditions.
- Misconception: “Volume must always be in liters.” The law is flexible; as long as units are consistent, you can use any unit of volume, like cubic meters or milliliters.
- Misconception: “Temperature needs to be in Celsius.” The law requires temperature in Kelvin to maintain proportional relationships, so always convert Celsius to Kelvin before calculations.
Based on what I’ve seen it can be tempting to fall into these pitfalls when you’re starting out. Keep in mind that honing your skills and being meticulous with units and conversions are crucial for getting the hang of this principle. Don’t allow these frequent mistakes to discourage you; with a touch of perseverance you’ll breeze through them smoothly.
Practical Tips for Using the Combined Gas Law
Utilizing the Combined Gas Law can be pretty easy if you keep some helpful suggestions in mind. Here’s a guide on how to maximize its usage
- Double-Check Units: Ensure all units are consistent, especially when dealing with temperature and volume. Convert temperatures to Kelvin and volumes to the same unit.
- Organize Your Data: Write down your initial and final conditions clearly before solving the problem. This helps avoid mistakes and keeps your work organized.
- Understand the Relationships: Familiarize yourself with how pressure, volume, and temperature interrelate. This will help you predict outcomes and solve problems more intuitively.
- Practice Regularly: Like any skill, proficiency comes with practice. Solve various problems to reinforce your understanding and application of the Combined Gas Law.
During my chemistry journey I discovered that having a checklist for these suggestions streamlined the process and reduced the pressure. Each piece of advice serves as a step towards grasping the Combined Gas Law turning intricate calculations into a more intuitive task.
Why Understanding This Law Matters
Grasping the Combined Gas Law goes beyond being a task; it plays a role in uncovering various real life events. I remember coming across this law for the time during an internship at a laboratory. We were engaged in a project related to reactions and understanding how to adjust pressure, volume and temperature was essential. The law assisted us in forecasting the behavior of gases under varying conditions, making our experiments safe and efficient.
Here’s why this knowledge is essential:
- Safety: In industries that use gases, like manufacturing or even the food and beverage industry, understanding gas laws helps prevent accidents caused by pressure changes.
- Efficiency: Accurate predictions of gas behavior lead to more efficient processes, whether you’re optimizing a chemical reaction or designing a new product.
- Real-World Applications: From airbags in cars to diving equipment, the principles of gas laws are used to design and operate a multitude of everyday items.
In summary getting a grip on the Combined Gas Law gives you an asset for tackling real world challenges and making well informed choices whether in school or in other areas of life.
FAQs About the Combined Gas Law
When it comes to the Combined Gas Law, newcomers often have queries. Here are some common questions along with my personal thoughts on them.
- What is the Combined Gas Law used for? It’s used to predict the behavior of gases when they undergo changes in pressure, volume, or temperature. It’s like a versatile tool that helps in various scientific and industrial applications.
- Do I need to use Kelvin for temperature? Yes, temperature must be in Kelvin for the Combined Gas Law to work correctly. Converting from Celsius to Kelvin is a small step that ensures accurate calculations.
- How do I remember the formula? Think of the formula as a recipe: it combines the ingredients from Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Gay-Lussac’s laws into one dish. Keeping this analogy in mind can help you recall the formula more easily.
- Can I use this law for real gases? While the law is based on the ideal gas model, it provides a good approximation for real gases under many conditions. For more precise calculations, corrections might be needed.
These frequently asked questions address concerns and can assist in enhancing your comprehension of the Combined Gas Law making it feel more accessible and less intimidating.
Wrapping It Up: Key Takeaways
As we conclude our journey into the Combined Gas Law let’s take a moment to recap the crucial aspects that will reinforce your comprehension. Looking back on my own experience with this subject I’ve come to appreciate the law’s true worth in its usefulness and adaptability.
- Integration of Laws: The Combined Gas Law is a fusion of Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Gay-Lussac’s laws, simplifying the study of gas behaviors into a single, cohesive formula.
- Practical Applications: Whether you’re a student, a professional in the chemical industry, or simply curious about how things work, this law provides valuable insights into the behavior of gases.
- Continuous Practice: Mastery comes with practice. Use the law in various scenarios to get comfortable with its applications and nuances.
Grasping and utilizing the Combined Gas Law is akin to possessing a that opens numerous pathways in both conceptual and real world contexts. It serves as a fundamental principle in chemistry bridging the gap between abstract concepts and practical uses. This makes it an essential asset for scientific exploration and everyday situations.