Enforcement of Lien Laws in California Explained
In the state of California, lien legislation is an essential factor in defending both creditors’ and property owners’ rights. A lien is a legal claim on property for unpaid debts. This allows creditors to secure their investment and guarantees that they will receive payment. Therefore, having a lien on your house can make selling or refinancing difficult.
The State of California has rigorous lien laws that offer detailed directions on the enforcement and contesting of liens. Property owners who comprehend these laws can legalize their entitlements and responsibilities properly. Homeowners, contractors or even the creditors must know about lien law so that they can protect their interests as well as comply with the state regulations.
Types of Liens in California

California acknowledges various categories of liens that perform distinct functions. Below are some of the most prevalent ones:
- Mechanic’s Liens: Filed by contractors or suppliers who have not been paid for work done or materials supplied on a property.
- Judgment Liens: Created when a court judgment is entered against a debtor, allowing the creditor to place a lien on the debtor’s property.
- Tax Liens: Imposed by the government for unpaid taxes. These can be serious, as they often take priority over other liens.
- Mortgage Liens: Created when a property owner borrows money against their property, using the property as collateral.
Because each lien requires certain particulars and undertakes distinct processes to execute, anyone who deals with liens should understand these differences.
How Liens are Created
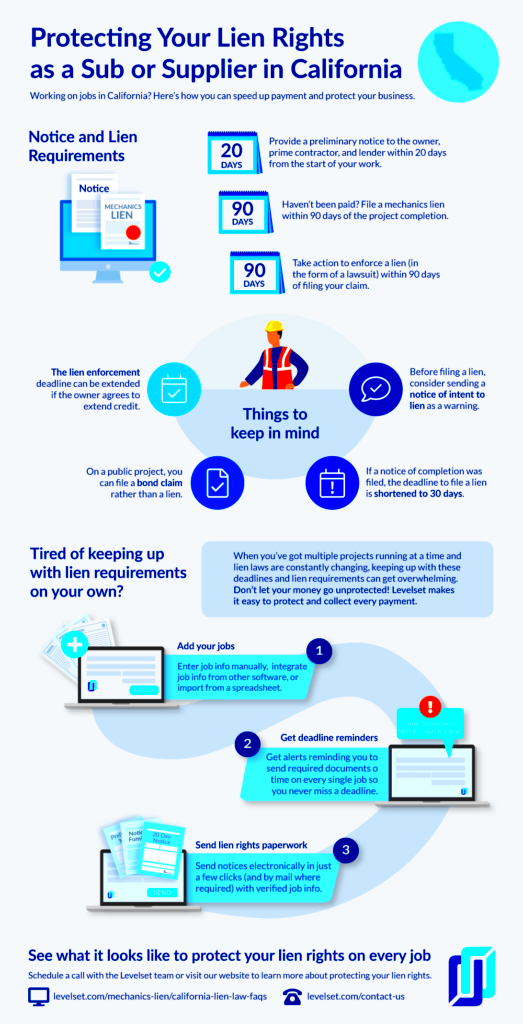
Depending on the kind of lien, it is created through different processes. Here is how they are usually born:
- Contractual Agreements: Many liens, like mechanic’s liens, are based on contracts. When a contractor performs work without payment, they can file a lien to secure their right to compensation.
- Court Judgments: For judgment liens, a creditor must first obtain a court judgment against the debtor. Once the judgment is awarded, the creditor can file the lien with the county recorder’s office.
- Tax Assessments: Tax liens arise when property taxes are not paid. The government will assess the property, and if taxes remain unpaid, a lien is automatically placed.
- Mortgage Documents: When a property owner takes out a mortgage, they sign a deed of trust, which creates a lien on the property in favor of the lender.
To ascertain its validity and enforceability, it is crucial that proper procedures are followed for every kind of lien. Complications later on may arise when a step is missed.
Enforcement Process for Liens

Processes for lien enforcement differ per the type of a lien in California; hence it is vital to comprehend them as creditors eyeing claim enforcement and property owners protecting their properties. When a lien is lodged in county recording offices, they will begin the process of recovering their debts depending on certain steps that must be followed by the creditor.
In terms of the common pattern by which law enforcement bodies typically enforce laws:
- Filing the Lien: The creditor files the lien with the county recorder, providing details about the debt and the property in question.
- Notice to the Property Owner: After filing, the creditor must usually provide notice to the property owner, informing them of the lien.
- Waiting Period: Depending on the type of lien, there may be a waiting period during which the property owner can resolve the debt.
- Foreclosure Proceedings: If the debt remains unpaid, the creditor can initiate foreclosure proceedings, which allows them to sell the property to recover the owed amount.
It is essential to mention that every category of lien includes unique guidelines and timeframes; therefore, seeking advice from an attorney may clarify what step should be taken next.
Challenges in Lien Enforcement
Enforcement of lien is more complicated than it appears, and complications can occur during the entire process. Once creditors and property owners understand these obstacles, they will be able to handle the situation better.
Among the familiar obstacles faced in lien enforcement are:
- Disputes Over Validity: Property owners may challenge the validity of the lien, leading to legal disputes that can prolong the enforcement process.
- Bankruptcy Claims: If the property owner files for bankruptcy, it can halt lien enforcement, as the bankruptcy court may prioritize the debtor’s obligations.
- Improper Filing: If the lien is not filed correctly or within the required timeframe, it may be deemed invalid, preventing enforcement.
- Market Conditions: Even when a lien is enforceable, unfavorable market conditions can make it difficult to sell the property at a price that covers the debt.
If stakeholders know these challenges, they can be better prepared and take proactive measures to safeguard their interests as well.
Legal Rights of Lien Holders
Grasping the legal entitlements of lien holders is crucial not only to the lenders but also to the proprietors. Such rights enable the holders of liens to be protected and pathways through which they can actualize their claims. In California, there are several particular rights that belong to lien holders:
- Right to Payment: Lien holders have the right to be paid for the services or goods provided before other creditors, depending on the lien type.
- Right to Foreclose: If the debt remains unpaid, lien holders can initiate foreclosure proceedings to recover the owed amount by selling the property.
- Right to File a Lawsuit: If a property owner disputes the lien, lien holders can file a lawsuit to establish the validity of the lien and seek a judgment in their favor.
- Right to Notice: Lien holders are entitled to receive notice of any proceedings related to the property, such as bankruptcy filings or foreclosure actions.
It’s true that these rights promote effective enforcement of claims by lien holders, still important is the knowledge of property owners on how to dispute or compromise such claims. Possession of equal information on each side fosters a more harmonious settlement.
Impact of Bankruptcy on Liens
The implications of filing for bankruptcy on existing liens can be vast and varied. Bankruptcy is a legal protection which can have implications for the rights of creditors, including lien holders. Both creditors wanting to enforce their claims and property owners wishing to preserve their properties must know how bankruptcy works with liens.
Below are some important aspects that should be looked at with respect to the effect of bankruptcies on liens:
- Automatic Stay: When bankruptcy is filed, an automatic stay goes into effect, halting all collection efforts, including lien enforcement. This means creditors must wait for the bankruptcy proceedings to resolve.
- Secured vs. Unsecured Creditors: Lien holders are typically considered secured creditors, meaning they have a legal claim to specific assets. In bankruptcy, secured creditors may have priority over unsecured creditors when debts are repaid.
- Potential for Lien Avoidance: In some cases, debtors may be able to avoid certain liens if they can prove that the lien is not valid or does not meet legal standards.
- Property Valuation: The value of the property subject to the lien will be assessed during bankruptcy proceedings. If the property’s value is less than the debt, the lien may be modified or stripped away.
In the end, bankruptcy’s impacts on liens can be intricate, and a legal expert’s assistance may help define the alternative courses open to the creditors and the debtors.
FAQs about Lien Laws in California
If you are dealing with a lien or thinking of filing one, it is normal to have questions regarding lien laws. Here are some questions that people frequently ask and which can help provide an understanding:
-
What is a lien?
- A lien is a legal claim against a property to secure the payment of a debt. It can affect the property owner’s ability to sell or refinance.
-
How long does a lien last in California?
- Generally, a lien lasts for 10 years but can be extended if necessary. It must be renewed to remain valid.
-
Can I remove a lien from my property?
- Yes, liens can be removed through payment of the debt, a court order, or by proving the lien is invalid.
-
Do I need a lawyer to file a lien?
- While it’s possible to file a lien without a lawyer, it’s advisable to seek legal assistance to ensure compliance with all legal requirements.
-
What happens if a lien is not enforced?
- If a lien is not enforced within a specific timeframe, it may lose its validity and cannot be enforced later.
Common concerns are highlighted in these FAQs and may assist you comprehend your legal rights and duties with respect to lien statutes in California.
Conclusion on Lien Enforcement in California
So, finally, for anyone who takes part in property ownership, contracting or lending, it is crucial to grasp lien enforcement in California. Creditors use liens as a vital means of securing their interests; however, they have intricacies that may greatly affect properties’ proprietors.
The enforcement process consists of specific steps, and challenges may be faced along the way, as we have examined. In addition, the interaction between liens and bankruptcy adds to the complexity that must be navigated carefully by creditors and debtors alike. Stakeholders are better able to manage these situations if they know about lien holders’ legal rights and understand the different types of liens.
In conclusion, lien statutes are important legal instruments for a creditor seeking to enforce an outstanding account or a property manager trying to shield his her possessions from being auctioned off. Therefore, it is important to know the use of liens when it comes to debts since they come in handy when trying to secure your funds or protect someone else’s money from other creditors. A knowledgeable attorney can give you some direction on what steps to take next if there’s a claim against your property.


