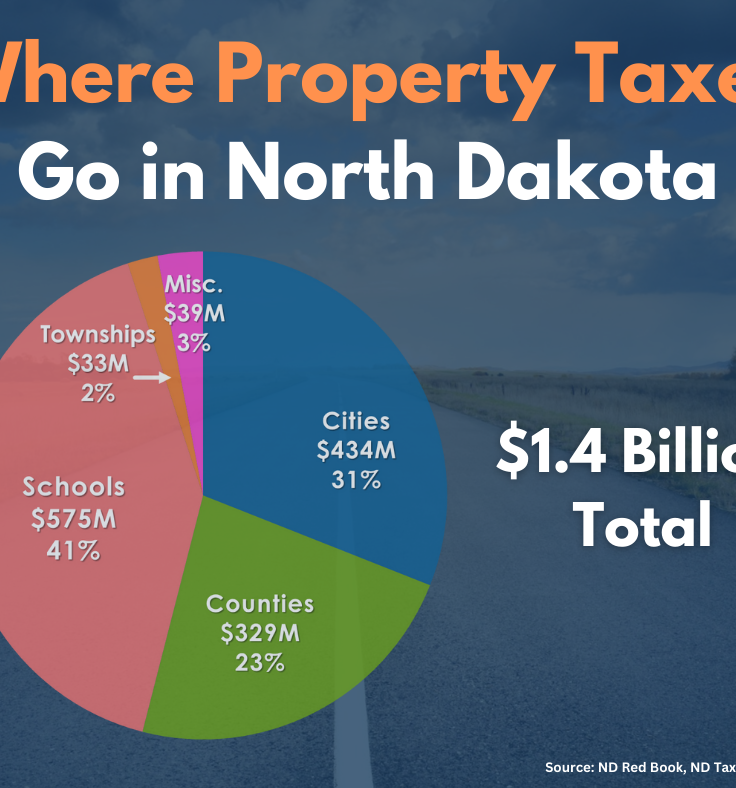
Essential Information About North Dakota Property Tax Laws
North Dakota property tax laws play a crucial role in funding local services like schools, roads, and emergency services. Understanding these laws can help property owners navigate the tax landscape effectively. In this post, we’ll break down key aspects of property taxes in North Dakota, including how assessments are made, available exemptions, and more. Whether you’re a homeowner or a potential buyer, it’s essential to grasp these laws to manage your property tax obligations wisely.
Understanding Property Tax Assessment
Property tax assessments in North Dakota are the process of determining the value of a property for tax purposes. Here’s how it works:
- Market Value: Assessors estimate the market value of properties based on various factors, such as location, size, and condition.
- Assessment Ratio: This is the percentage of the property’s market value that is subject to taxation. In North Dakota, the assessment ratio is typically set at 100% for residential properties.
- Annual Assessments: Property values can change yearly due to market fluctuations, so assessments are updated regularly.
Homeowners receive an assessment notice that outlines their property’s value. If you believe your property has been overvalued, you can appeal the assessment through your local tax authority.
Property Tax Exemptions in North Dakota
North Dakota offers several property tax exemptions that can significantly reduce the tax burden for eligible property owners. Here are some common exemptions:
- Homestead Exemption: Homeowners may qualify for a homestead exemption if they occupy the property as their primary residence. This exemption can lower the taxable value of the home.
- Veterans Exemption: Veterans and their surviving spouses may be eligible for additional exemptions on their property taxes, reducing the financial impact.
- Senior Citizen Exemption: Seniors aged 65 and older can benefit from a property tax exemption that provides significant savings.
- Disabled Individual Exemption: Individuals with disabilities may also qualify for exemptions that reduce their property tax obligations.
It’s essential to check with your local tax assessor’s office to understand the specific eligibility requirements for these exemptions. Applying for an exemption can be a straightforward process, often requiring proof of eligibility and a completed application form.
Property Tax Rates and Calculation
Understanding property tax rates and how they’re calculated is crucial for every property owner in North Dakota. Property tax rates can vary by county, and they are expressed as a percentage of the assessed value of your property. Here’s how the calculation typically works:
- Assessed Value: This is determined by your local assessor based on the market value of your property. As mentioned earlier, the assessment ratio is generally 100% in North Dakota.
- Mill Rate: The mill rate is the amount per $1,000 of assessed value that you pay in taxes. For example, a mill rate of 100 means you pay $100 in taxes for every $1,000 of assessed value.
- Tax Calculation Formula: To calculate your property tax, you can use the formula: Tax Amount = (Assessed Value / 1000) x Mill Rate.
It’s a good idea to check your local county’s tax website for the current mill rate, as these can change annually based on local budgets and needs. Keep in mind that understanding how these factors work together can help you better manage your property taxes and avoid surprises when bills come due.
Payment Options for Property Taxes
When it comes to paying your property taxes in North Dakota, you have several options that can make the process easier. Here’s what you need to know:
- Annual Payment: Most property taxes are due annually, typically in December. You can pay the full amount at once.
- Installment Payment: Some counties allow property owners to pay their taxes in installments. This can help spread out the financial burden.
- Online Payment: Many counties offer online payment options. This is often the easiest and fastest way to pay your taxes. Check your county’s website for details.
- Mail-In Payments: You can also send a check or money order by mail. Just make sure to send it well before the due date to avoid penalties.
Always keep your receipts and records of payment. This documentation can be helpful for future reference or if any issues arise regarding your property taxes.
Appealing Property Tax Assessments
If you believe your property has been overvalued, you have the right to appeal your property tax assessment in North Dakota. Here’s how the appeal process generally works:
- Review Your Assessment: First, carefully review your property assessment notice. Check the assessed value and the details provided.
- Gather Evidence: Collect information to support your case, such as comparable property sales, photographs, or other relevant data that shows your property’s value is lower than assessed.
- File an Appeal: Contact your local assessor’s office to find out how to file an appeal. This usually involves filling out a form and submitting your evidence.
- Attend the Hearing: After filing, you may be scheduled for a hearing where you can present your case to the local Board of Equalization or a similar authority.
It’s essential to pay attention to deadlines for filing appeals, as these can vary by county. A successful appeal can lead to a reduction in your property tax bill, so it’s worth the effort if you feel your assessment is incorrect.
Consequences of Not Paying Property Taxes
Not paying your property taxes can lead to some serious consequences in North Dakota. It’s essential to understand what could happen if you miss a payment. Here’s what you need to know:
- Late Fees and Penalties: If you fail to pay your property taxes by the due date, you will likely incur late fees and penalties. These can add up quickly, increasing your total tax bill.
- Tax Liens: Unpaid property taxes can lead to a tax lien being placed on your property. This means that the county has a legal claim against your property until the taxes are paid.
- Tax Sale: If property taxes remain unpaid for an extended period, the county may auction your property at a tax sale to recover the owed amount. This could result in the loss of your home or investment property.
- Impact on Credit Score: Unpaid property taxes can negatively affect your credit score, making it harder to secure loans or mortgages in the future.
To avoid these consequences, it’s crucial to stay on top of your property tax payments. If you’re struggling to pay, reach out to your local tax office to discuss possible payment plans or assistance programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions property owners in North Dakota often ask about property taxes:
- What is the property tax deadline in North Dakota? Property taxes are usually due in December, but specific dates can vary by county. Always check with your local tax authority for precise dates.
- Can I appeal my property tax assessment? Yes, if you believe your property is overvalued, you can appeal the assessment. Be sure to gather evidence to support your case.
- Are there any exemptions available? Yes, North Dakota offers various exemptions for homesteads, veterans, seniors, and individuals with disabilities. Check with your local assessor for eligibility requirements.
- What happens if I miss a property tax payment? If you miss a payment, you may incur late fees, and your property could be subject to a tax lien or sale.
Always stay informed about your rights and obligations regarding property taxes to avoid any unpleasant surprises.
Conclusion on North Dakota Property Tax Laws
Understanding North Dakota property tax laws is vital for every property owner. By knowing how assessments are made, what exemptions are available, and the consequences of not paying your taxes, you can navigate the system more effectively. Remember to keep track of important deadlines and stay in communication with your local tax authority. If you’re facing challenges, don’t hesitate to seek help or appeal assessments. Being proactive can save you money and ensure your rights as a property owner are protected. By staying informed and engaged, you can make the most of your property ownership experience.