Arkansas Franchise Law Explained for Business Owners
Franchise law in Arkansas is crucial for anyone considering entering a franchise business. It governs the relationship between franchisors and franchisees, ensuring that both parties understand their rights and responsibilities. The law aims to protect potential franchisees from unfair practices while providing a framework for franchisors to operate legally. Familiarizing yourself with these laws can help you navigate the complex world of franchising and make informed decisions for your business.
Key Components of Franchise Agreements
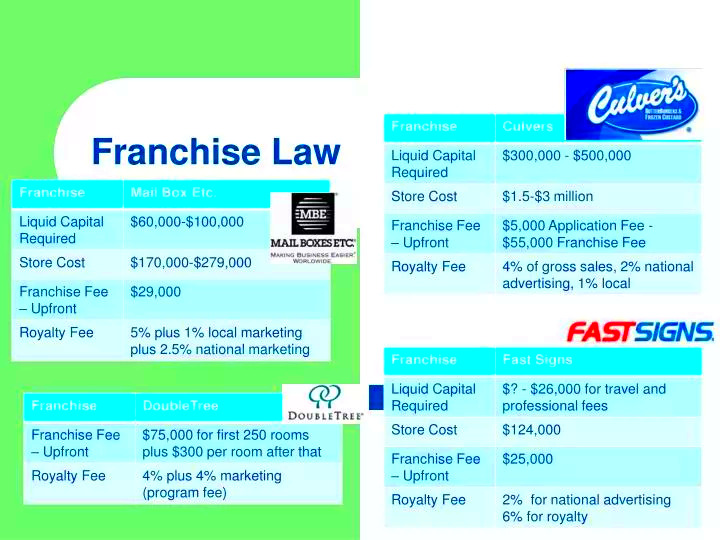
A franchise agreement is a vital document that outlines the relationship between the franchisor and franchisee. Understanding its key components can save you from potential disputes down the line. Here are the main elements:
- Grant of Franchise: This section defines the rights granted to the franchisee, including the use of trademarks and business systems.
- Fees and Royalties: This outlines initial franchise fees, ongoing royalties, and any other financial obligations.
- Term of Agreement: The duration of the franchise agreement and conditions for renewal are specified here.
- Territory: This defines the geographic area where the franchisee can operate, protecting them from competition from other franchisees.
- Training and Support: This details the training programs provided by the franchisor and ongoing support.
- Termination Clause: This outlines conditions under which the agreement can be terminated by either party.
Franchise Disclosure Document Requirements

The Franchise Disclosure Document (FDD) is a crucial document that franchisors must provide to potential franchisees. In Arkansas, the FDD must comply with both federal and state laws. Here’s what you need to know:
- Overview of the Business: The FDD must provide information about the franchisor, including its history and business experience.
- Financial Performance: While not required, many franchisors include earnings claims to give potential franchisees an idea of potential profitability.
- Franchise Fees: The FDD must clearly outline all costs involved in starting and operating the franchise.
- Legal Issues: Disclosure of any current or past legal issues involving the franchisor or its executives is mandatory.
- Franchisee Obligations: The FDD should detail what is expected from franchisees, including operational requirements and compliance with standards.
Understanding the FDD is essential for making an informed decision. It provides transparency and helps franchisees assess the risks and benefits of investing in a franchise.
Registration and Filing Procedures for Franchisors

In Arkansas, franchisors must follow specific registration and filing procedures to operate legally. Understanding these steps is essential for compliance and smooth business operations. The registration process ensures that franchisors meet all legal requirements, providing protection for franchisees. Here’s a breakdown of what franchisors need to do:
- Prepare the Franchise Disclosure Document (FDD): The FDD must be accurate, comprehensive, and compliant with state and federal laws.
- Submit Registration Application: Franchisors must submit a registration application to the Arkansas Securities Department.
- Pay Filing Fees: There is typically a filing fee associated with the registration process, which can vary based on the type of franchise.
- Provide Supporting Documentation: Additional documents may be required, including financial statements, agreements, and corporate documents.
- Await Approval: Once submitted, the application will be reviewed by the state. Franchisors should be prepared for potential follow-up questions or requests for additional information.
Completing these steps correctly can help franchisors avoid legal complications and establish a solid foundation for their franchise operations in Arkansas.
Legal Rights and Obligations of Franchisees
Franchisees have specific legal rights and obligations that help define their relationship with the franchisor. Understanding these can empower franchisees and ensure they protect their investments. Here’s what franchisees need to know:
- Right to Receive Information: Franchisees have the right to receive clear and complete information about the franchise, including the FDD.
- Right to Fair Treatment: Franchisees should be treated fairly and equitably by the franchisor, with respect for their territory and investment.
- Obligation to Follow Standards: Franchisees are required to adhere to the operational standards set by the franchisor to maintain brand consistency.
- Financial Obligations: Franchisees must pay all required fees and royalties on time, as outlined in the franchise agreement.
- Right to Renew: Franchisees often have the right to renew their franchise agreement, subject to the terms set by the franchisor.
Being aware of these rights and obligations can help franchisees navigate their responsibilities and ensure a positive business relationship with their franchisor.
Common Issues in Franchise Relationships
Franchise relationships can sometimes be tricky, and various issues may arise over time. Being aware of these common challenges can help both franchisors and franchisees address them proactively. Here are some of the frequent issues:
- Non-compliance with Standards: Franchisees may struggle to meet the operational standards set by the franchisor, leading to conflicts.
- Financial Disputes: Issues related to fees, royalties, or additional costs can cause friction between the two parties.
- Termination of Agreements: Disagreements over the terms of termination can lead to legal battles, particularly if franchisees feel wronged.
- Brand Reputation Concerns: If one franchisee does not uphold the brand standards, it can negatively impact the entire franchise’s reputation.
- Lack of Support: Franchisees may feel they are not receiving adequate support from the franchisor, leading to dissatisfaction.
Open communication and a solid understanding of the franchise agreement can help mitigate these issues, fostering a healthy franchise relationship.
Franchise Termination and Renewal Process
Understanding the franchise termination and renewal process is crucial for both franchisors and franchisees. This knowledge helps both parties prepare for changes and ensures they know their rights and responsibilities. Termination can occur for various reasons, while renewal involves specific steps to continue the business relationship. Here’s a closer look at the process:
- Grounds for Termination: Franchisors can terminate agreements for reasons like failure to meet operational standards, non-payment of fees, or breaches of contract. Franchisees should be aware of these conditions to avoid unexpected terminations.
- Notice Requirements: Most agreements stipulate a notice period that must be followed before termination can take effect. Typically, this can range from 30 to 90 days.
- Opportunity to Cure: In many cases, franchisees are given a chance to resolve issues before termination is finalized, allowing them to fix problems.
- Renewal Terms: Franchise agreements often include specific conditions for renewal, such as adherence to updated standards or payment of renewal fees.
- Documentation: Both parties should maintain clear records of all communications and agreements related to termination and renewal to avoid misunderstandings.
Understanding these processes can help both franchisors and franchisees navigate the end of their agreements or ensure a smooth transition into renewal.
Frequently Asked Questions About Franchise Law
Many questions arise when discussing franchise law, especially for those new to franchising. Here are some frequently asked questions to provide clarity:
- What is a Franchise? A franchise is a business model where a franchisor grants a franchisee the right to operate a business using its brand and systems.
- What is the Franchise Disclosure Document? The FDD provides potential franchisees with essential information about the franchise, including fees, obligations, and legal history.
- Are franchise agreements negotiable? While some terms may be negotiable, key elements like franchise fees and royalty structures are often set by the franchisor.
- What should I do if I believe my franchisor is not complying with the agreement? Document your concerns and attempt to resolve the issue with your franchisor. If unresolved, consider seeking legal advice.
- Can I sell my franchise? Yes, but most franchise agreements require you to notify the franchisor and may have specific conditions for resale.
These questions address some common concerns, but consulting a legal professional is always a good idea for personalized advice.
Conclusion on Franchise Law in Arkansas
Franchise law in Arkansas plays a vital role in the relationship between franchisors and franchisees. Understanding the legal framework helps both parties navigate their rights and responsibilities effectively. From the initial disclosure requirements to the complexities of termination and renewal, having a solid grasp of the laws ensures smoother operations and protects investments. Whether you’re considering a franchise or already in one, staying informed about your rights and obligations is essential. With the right knowledge, you can build a successful and sustainable franchise business in Arkansas.