Criminal Law Examples and Explanations Explained
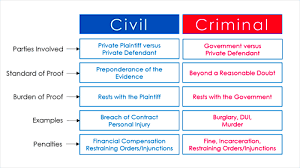
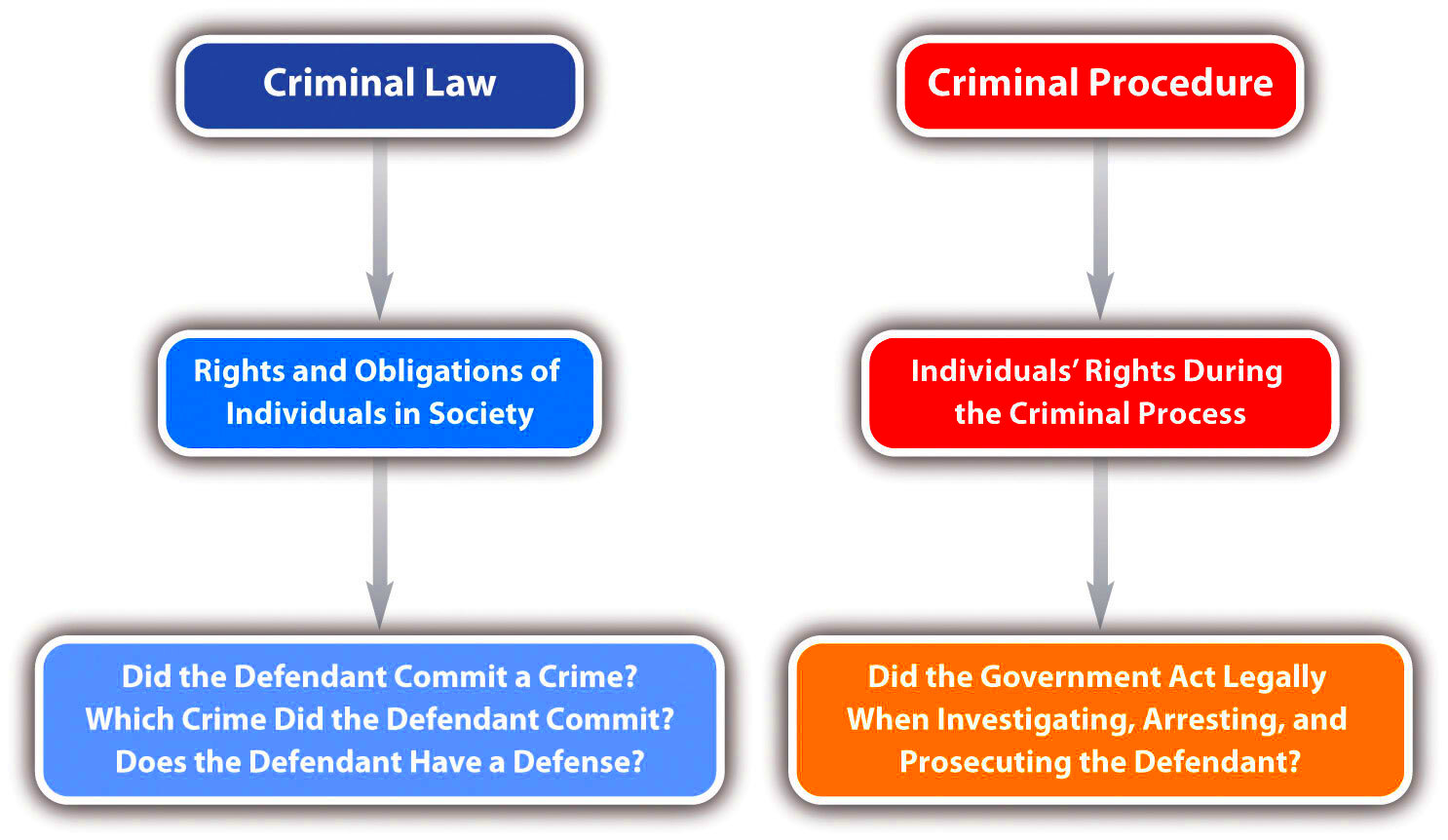
Criminal law is the body of law that pertains to crime. It defines criminal offenses, establishes penalties, and regulates the process for apprehending, charging, and trying suspected offenders. Essentially, criminal law serves to protect society by punishing harmful behavior. It is essential for maintaining order and ensuring justice. When someone commits a crime, they violate the laws set forth by the government, which can lead to serious consequences.
Types of Criminal Offenses

Criminal offenses can be categorized in various ways. Understanding these categories helps clarify the nature of the crime and its potential consequences. Here are the primary types of criminal offenses:
- Personal Crimes: These crimes directly harm individuals, such as assault, robbery, and homicide.
- Property Crimes: Crimes that involve the theft or destruction of someone else’s property, including burglary and vandalism.
- White-Collar Crimes: Non-violent crimes committed for financial gain, such as fraud and embezzlement.
- Victimless Crimes: Offenses where there is no direct victim, such as drug use and gambling.
Each type of offense carries its own set of penalties and legal implications, affecting how the law is applied in different situations.
Felonies and Misdemeanors Explained
Criminal offenses are often classified into two main categories: felonies and misdemeanors. This classification is important because it determines the severity of the punishment. Here’s a breakdown of each:
| Type of Offense | Definition | Examples | Potential Punishment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Felony | Serious crimes usually punishable by imprisonment for over one year. | Murder, rape, armed robbery | Prison time, fines, loss of civil rights |
| Misdemeanor | Less serious offenses generally punishable by less than one year in jail. | Theft, simple assault, vandalism | Jail time, fines, community service |
Understanding these classifications is crucial for anyone involved in a criminal case. They influence the legal strategy, potential outcomes, and the rights of the accused.
Key Elements of a Crime

To understand criminal law, it’s essential to know the key elements that define a crime. Each crime typically consists of specific components that must be proven for someone to be found guilty. These elements help establish whether the accused truly committed the offense. Let’s break them down:
- Actus Reus: This is the physical act of committing a crime. It can be an action or a failure to act when there’s a legal duty to do so.
- Mens Rea: This refers to the mental state or intent of the person committing the crime. It addresses whether the individual acted knowingly, recklessly, or with intent.
- Causation: There must be a clear link between the act and the harm caused. This element establishes that the act directly resulted in the outcome.
- Harm: A crime must cause harm to a person, property, or society. This element confirms that the act has a negative impact.
- Legality: The behavior must be defined as a crime by law. This means that what may be considered immoral isn’t necessarily illegal unless stated by law.
These key elements play a critical role in the prosecution’s case and the defense strategy in a criminal trial. Understanding them can provide valuable insights into how criminal cases unfold.
Examples of Common Criminal Offenses
Criminal law encompasses a wide range of offenses, each with unique characteristics and consequences. Here are some common examples, categorized for clarity:
- Violent Crimes:
- Assault
- Robbery
- Murder
- Property Crimes:
- Burglaries
- Theft
- Arson
- White-Collar Crimes:
- Fraud
- Embezzlement
- Insider trading
- Drug Crimes:
- Possession
- Trafficking
- Manufacturing
Each of these offenses carries different penalties and legal repercussions, reflecting their severity. Understanding these common offenses can help individuals navigate the complexities of criminal law more effectively.
Defenses in Criminal Law
In criminal law, defendants have the right to present defenses that challenge the prosecution’s case. The goal of a defense is to create reasonable doubt about the defendant’s guilt. Here are some common defenses used in criminal cases:
- Self-Defense: Claiming that the crime was committed to protect oneself from harm.
- Insanity Defense: Arguing that the defendant was not in a sound mental state at the time of the crime.
- Alibi: Providing evidence that the defendant was elsewhere when the crime occurred.
- Entrapment: Claiming that law enforcement induced the defendant to commit the crime.
- Consent: Asserting that the victim agreed to the act, negating the claim of a crime.
These defenses can significantly influence the outcome of a case. A skilled attorney will evaluate the circumstances and choose the most appropriate defense strategy, helping to ensure that justice is served.
Role of Law Enforcement in Criminal Cases
Law enforcement plays a crucial role in the criminal justice system, acting as the first line of defense against crime. Their responsibilities encompass a range of activities that ensure public safety and uphold the law. Understanding these roles helps clarify how the system operates and what citizens can expect from law enforcement. Here’s a breakdown of their key functions:
- Investigation: Officers gather evidence and investigate crimes, often interviewing witnesses and collecting forensic evidence.
- Arrest: When there’s probable cause, law enforcement can arrest suspects, taking them into custody for alleged criminal activities.
- Patrolling: Regular patrols help deter crime and provide a visible presence in the community, promoting safety.
- Enforcement: Officers enforce laws by issuing citations for violations, such as traffic offenses or minor infractions.
- Collaboration: Law enforcement often collaborates with other agencies, such as prosecutors and social services, to effectively manage cases.
The effectiveness of law enforcement can greatly influence the outcome of criminal cases. Their actions during investigations can determine whether a case goes to trial, impacting both victims and suspects.
Importance of Legal Representation
Having legal representation in criminal cases is vital for anyone accused of a crime. An attorney serves as a defender of rights, guiding the accused through the complexities of the legal system. Here are some reasons why legal representation is essential:
- Expertise: Attorneys understand the law and can provide valuable insights into the legal process, potential defenses, and consequences.
- Protection of Rights: A lawyer ensures that the defendant’s rights are protected throughout the legal proceedings, from arrest to trial.
- Negotiation: Legal representation can lead to plea bargains or reduced charges, minimizing potential penalties.
- Trial Preparation: A skilled attorney prepares the defense strategy, gathers evidence, and selects witnesses, increasing the chances of a favorable outcome.
- Emotional Support: Facing criminal charges can be overwhelming. An attorney provides support and guidance, helping clients navigate stress and anxiety.
In short, having an attorney can make a significant difference in the outcome of a criminal case, ensuring that the accused receives fair treatment and representation.
FAQs
In the world of criminal law, questions often arise about processes, rights, and responsibilities. Here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify common concerns:
- What should I do if I am arrested?If you are arrested, remain calm and do not resist. Exercise your right to remain silent and request an attorney immediately.
- What is the difference between a felony and a misdemeanor?A felony is a more serious crime, often punishable by imprisonment for over a year, while a misdemeanor is less severe and usually results in shorter jail time.
- Can I represent myself in a criminal case?While you have the right to represent yourself, it is not recommended due to the complexities of the law and potential consequences.
- What happens during a plea bargain?A plea bargain is an agreement where the defendant pleads guilty to a lesser charge in exchange for a reduced sentence or dropped charges.
- How long does a criminal trial take?The duration of a trial can vary widely, but it typically lasts from a few days to several weeks, depending on the case complexity.
Understanding these aspects of criminal law can empower individuals facing charges, helping them make informed decisions throughout the legal process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the basics of criminal law is essential for anyone navigating the legal system. From grasping the key elements of a crime to recognizing the role of law enforcement and the importance of legal representation, knowledge is power. Being aware of common criminal offenses and potential defenses can make a significant difference in how individuals respond to accusations. Legal matters can be complex, but having a clear understanding of these concepts helps individuals make informed decisions and seek justice effectively. If you or someone you know is facing legal issues, don’t hesitate to reach out to a qualified attorney for guidance and support.