Florida Lunch Break Laws in 2024 What You Should Know
Florida lunch break laws are essential for both employers and employees. These laws ensure that workers receive adequate time to rest and recharge during their workday. Understanding these regulations can help employees know their rights and help employers comply with state requirements. In this blog post, we will delve into the key aspects of lunch break laws in Florida, including legal requirements, duration, exceptions, and employee rights.
Legal Requirements for Lunch Breaks

In Florida, the legal requirements for lunch breaks can sometimes be confusing. Unlike many other states, Florida does not mandate specific laws regarding lunch breaks for adult employees. However, employers are encouraged to provide meal breaks. Here are a few important points to consider:
- Employees working more than 6 hours may be offered a meal break.
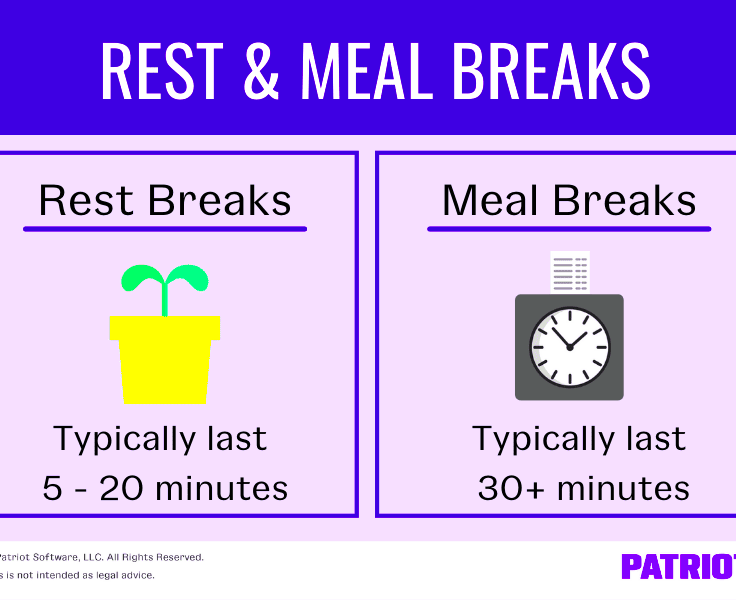
- If an employer provides a meal break, it should typically last at least 30 minutes.
- Employers are not required to pay employees for meal breaks as long as the employee is relieved of their duties.
It’s important to check any additional company policies or union agreements that might offer more generous terms than state law requires.
Duration of Lunch Breaks in Florida
The duration of lunch breaks in Florida can vary based on employer policies rather than strict state mandates. While Florida law does not specify the duration of breaks, here are some general practices:
| Work Duration | Typical Lunch Break Duration |
|---|---|
| Up to 6 hours | Not required but often none |
| 6 to 8 hours | 30 to 60 minutes |
| More than 8 hours | At least 30 minutes, typically 1 hour |
Remember, the specifics can vary significantly from one workplace to another. Employees should always check with their employers regarding the company’s policy on lunch breaks.
Exceptions to the Lunch Break Rules
While Florida law encourages lunch breaks, there are some exceptions where these rules may not apply. Understanding these exceptions can help both employers and employees navigate their rights and responsibilities. Here are a few key exceptions:
- Small Businesses: Employers with fewer than 5 employees may have more flexibility in providing breaks.
- Workplace Nature: Jobs that require constant monitoring, like security personnel or certain healthcare roles, might not allow for regular breaks.
- Employee Agreements: If an employee has a specific contract that outlines different break schedules, that agreement will typically take precedence over general guidelines.
- Emergency Situations: In urgent situations, such as medical emergencies or significant operational demands, employees may forgo breaks.
Employers should communicate any exceptions clearly to their employees, ensuring everyone understands their rights and responsibilities under these circumstances.
Employee Rights During Lunch Breaks
Employees have certain rights when it comes to lunch breaks, even if the state does not mandate specific break times. Here’s a rundown of what employees should know:
- Right to a Break: Employees should be informed about the company’s policy on lunch breaks.
- Uninterrupted Time: If a meal break is provided, employees should be free from work duties during this time.
- Right to Choose: Employees can usually decide how to use their break, whether that’s eating, resting, or stepping outside.
- Reporting Violations: If breaks are not provided as promised, employees can report this to HR or labor authorities.
Being aware of these rights empowers employees to advocate for themselves and ensure they receive the necessary breaks to maintain their well-being.
Employer Responsibilities for Lunch Breaks
Employers have specific responsibilities regarding lunch breaks to maintain a fair and productive workplace. Here’s what employers should keep in mind:
- Clear Communication: Employers must clearly communicate break policies to all employees, ensuring everyone understands their rights.
- Providing Breaks: While not legally required, offering reasonable breaks can enhance employee morale and productivity.
- Documenting Policies: It’s essential for employers to document their break policies in employee handbooks or company policies.
- Monitoring Compliance: Employers should regularly check that employees are receiving their entitled breaks and address any violations promptly.
By fulfilling these responsibilities, employers can create a positive work environment and comply with best practices in employee management.
Consequences of Violating Lunch Break Laws
Violating lunch break laws, even in a state like Florida where there aren’t strict mandates, can lead to serious consequences for employers. Understanding these repercussions is crucial for maintaining a compliant workplace. Here are some possible outcomes of non-compliance:
- Legal Action: Employees may file complaints with labor boards or take legal action if they feel their rights are violated, leading to potential lawsuits.
- Fines and Penalties: While Florida has fewer regulations, violating labor laws can result in fines from state or federal agencies.
- Loss of Employee Trust: When employers fail to provide promised breaks, it can lead to decreased morale and trust among employees, impacting overall productivity.
- Reputation Damage: Companies known for poor treatment of employees may struggle to attract and retain top talent.
It’s vital for employers to understand these risks and ensure compliance with any applicable lunch break guidelines, promoting a healthy workplace culture.
Best Practices for Employers Regarding Lunch Breaks
Implementing best practices around lunch breaks can foster a positive work environment and enhance employee satisfaction. Here are some effective strategies for employers:
- Establish Clear Policies: Write clear, concise policies regarding lunch breaks and communicate them to all employees.
- Encourage Regular Breaks: Promote a culture where taking breaks is encouraged, ensuring employees understand its importance for productivity and well-being.
- Be Flexible: Allow employees to choose their break times, if possible, to accommodate personal preferences and workloads.
- Provide Break Rooms: Create a comfortable break area where employees can relax and recharge.
By following these best practices, employers can create a supportive environment that prioritizes employee health and productivity.
FAQs About Florida Lunch Break Laws
Have questions about lunch break laws in Florida? Here are some frequently asked questions that might help clarify any uncertainties:
- Are employers required to give lunch breaks in Florida? No, Florida does not mandate lunch breaks, but employers are encouraged to provide them.
- How long should lunch breaks be? While there’s no set duration, a typical break ranges from 30 to 60 minutes for shifts longer than 6 hours.
- Can employers penalize employees for taking breaks? No, employees should not be penalized for taking their designated breaks. Doing so could violate labor laws.
- What should I do if my employer doesn’t allow breaks? Employees should first discuss the issue with their supervisor or HR. If the problem persists, they can file a complaint with the labor board.
These FAQs aim to clarify common concerns regarding lunch breaks in Florida and empower both employers and employees with the knowledge they need.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding Florida lunch break laws is crucial for both employers and employees. While the state does not mandate specific break times, promoting a culture that values lunch breaks can significantly enhance workplace morale and productivity. Employers should be proactive in communicating their break policies and ensuring compliance to avoid potential legal issues and foster a positive work environment. Employees, on the other hand, should be aware of their rights regarding breaks and advocate for their needs. By working together, both parties can create a healthier, more productive workplace.