An Overview of Security Guard Labor Law Compliance
Security guards play a vital role in maintaining safety, but ensuring their rights under labor laws is just as important. Compliance with labor laws helps protect both employers and employees, providing a framework for fair treatment in terms of wages, hours, and working conditions. This post explores the key aspects of labor law compliance specific to security guards, ensuring a balanced approach to employment. Understanding these laws can help both parties avoid legal issues while promoting a fair working environment.
Key Labor Laws for Security Guards

Security guards are covered by various labor laws that ensure fair treatment in the workplace. These laws address critical issues like minimum wage, overtime, rest breaks, and safety conditions. Below are some of the key labor laws:
- Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA): Sets standards for wages and overtime pay.
- Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA): Ensures a safe and healthy working environment.
- State-specific Labor Laws: Vary depending on the location, affecting wages, breaks, and other working conditions.
- Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO): Protects against discrimination based on race, gender, age, and more.
Understanding these laws ensures security guards are paid fairly and work under safe conditions. Employers need to stay informed about federal and state regulations to remain compliant.
Wages and Overtime Requirements
Wage and overtime laws ensure that security guards are compensated fairly for their time on the job. Under the FLSA, security guards must receive at least the federal minimum wage, and if they work more than 40 hours per week, they are entitled to overtime pay at a rate of 1.5 times their regular hourly wage.
| Hours Worked | Regular Pay | Overtime Pay |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 40 hours | Regular hourly rate | – |
| Over 40 hours | Regular hourly rate | 1.5 times regular rate |
Employers must track hours accurately to ensure compliance with overtime regulations. Failure to do so can lead to legal consequences, including fines or lawsuits.
Rest Breaks and Meal Periods
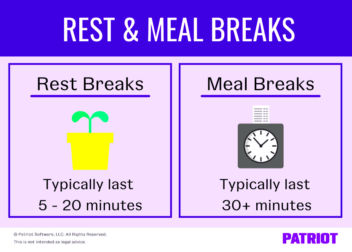
Rest breaks and meal periods are crucial for security guards to maintain focus and well-being during long shifts. Labor laws ensure that security guards receive proper breaks to avoid burnout and health issues. While these regulations may vary by state, certain rules are consistent across most regions.
For example, security guards are generally entitled to:
- Rest breaks: Typically, a 10-15 minute paid break for every 4 hours of work.
- Meal periods: A 30-minute unpaid meal break if the shift exceeds 5 hours.
- State-specific variations: Some states require additional rest or meal periods based on the number of hours worked.
It’s important for employers to schedule these breaks to comply with state and federal laws. Failing to provide required breaks could lead to legal penalties. Security guards also have the responsibility to take their breaks as scheduled, ensuring both their well-being and the employer’s compliance.
Working Conditions and Safety Standards
Ensuring the safety and proper working conditions for security guards is another key component of labor law compliance. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) sets standards for a safe working environment, which all employers must follow.
Security guards face unique challenges that may include:
- Exposure to hazards: Including physical confrontations or unsafe locations.
- Training requirements: Employers must provide necessary safety and emergency response training.
- Equipment: Guards must be provided with appropriate safety gear, such as uniforms, communication devices, and protective gear.
In addition to following OSHA guidelines, employers must address specific safety needs that apply to the environments where their security guards work. Regular safety checks, adequate training, and up-to-date equipment are essential for preventing injuries and ensuring compliance with labor laws.
Employment Contracts and Agreements
Employment contracts are a vital part of the relationship between security guards and their employers. These contracts outline the terms and conditions of employment, providing clear guidelines on expectations, compensation, and other key details.
A well-drafted employment contract should include:
- Job duties: A clear outline of the security guard’s responsibilities.
- Compensation: Details about wages, overtime, and any benefits offered.
- Working hours: The expected number of hours per week, including any on-call or overtime requirements.
- Termination terms: Conditions under which either party can terminate the contract.
- Non-compete clauses (if applicable): To prevent guards from working for competitors within a certain timeframe after employment ends.
These agreements not only protect the rights of the security guards but also help employers ensure that there is no ambiguity in employment terms. Clear contracts lead to smoother relationships and fewer legal disputes down the line.
Legal Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to comply with labor laws can have serious legal and financial repercussions for both employers and security guards. Non-compliance can lead to lawsuits, fines, and damage to a company’s reputation. It is essential for employers to understand the potential consequences of violating labor regulations and for security guards to be aware of their rights under these laws.
Common legal consequences of non-compliance include:
- Fines and penalties: Employers can face significant fines for failing to adhere to wage laws, overtime regulations, and safety standards.
- Employee lawsuits: Security guards may file lawsuits for unpaid wages, denied overtime, or unsafe working conditions, leading to costly legal battles.
- Back pay and compensation: Employers may be required to compensate employees for unpaid wages, overtime, or denied breaks, including interest on the amounts owed.
- Reputation damage: Negative publicity surrounding labor law violations can harm a company’s reputation, making it harder to attract clients and employees.
To avoid these consequences, employers should ensure they are fully compliant with labor laws and maintain proper documentation of work hours, wages, and working conditions. This helps protect both the employer and the security guards from future disputes or legal issues.
FAQs About Security Guard Labor Law Compliance
Understanding labor laws can be complex, and both employers and employees often have questions. Here are some frequently asked questions to clarify common concerns about security guard labor law compliance:
- Are security guards entitled to overtime pay? Yes, security guards are entitled to overtime pay for any hours worked beyond 40 in a week, usually at 1.5 times their regular hourly rate.
- What should I do if I am not being paid properly? If a security guard is not receiving fair wages or overtime, they should first speak to their employer. If the issue is not resolved, filing a complaint with the Department of Labor or seeking legal advice may be necessary.
- Are security guards entitled to rest breaks and meal periods? Yes, most states require employers to provide rest breaks and meal periods based on the length of the shift. The specific requirements vary by state.
- What happens if an employer violates labor laws? Employers can face fines, lawsuits, and may be required to pay back wages to employees who were wrongfully denied proper compensation or working conditions.
Conclusion on Security Guard Labor Law Compliance
Compliance with security guard labor laws is crucial for creating a fair and safe work environment. Whether it involves wages, overtime, rest breaks, or safety standards, both employers and employees have responsibilities to ensure these laws are followed. Employers must stay up-to-date with federal and state regulations, while security guards should be aware of their rights. Failure to comply with these laws can lead to severe legal and financial consequences. By following the rules, both parties can enjoy a more harmonious and legally secure workplace.