Charles’s Law Worksheet Answers for Better Understanding
Charles’s Law is one of those fundamental concepts in chemistry that connects the dots between temperature and volume in gases. I remember first encountering it during my school days and it felt like a revelation – understanding how the volume of a gas changes with temperature was like uncovering a hidden rule of nature. Its named after Jacques Charles, a French scientist whose experiments in the century laid the groundwork for this law. Charless Law essentially states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature provided the pressure remains constant. Its a simple yet profound principle that has practical implications in various fields from meteorology to engineering.
Basic Principles of Charles’s Law
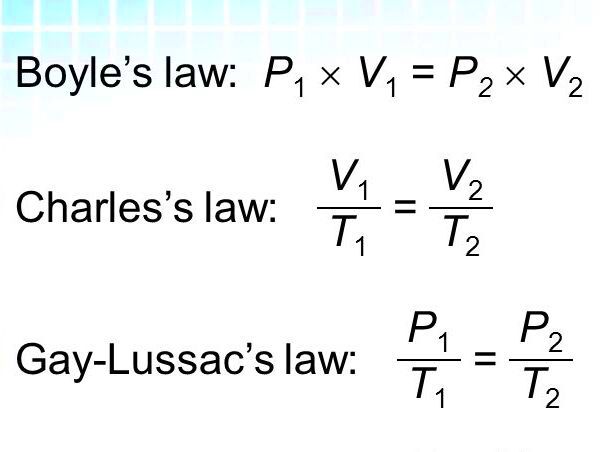
Charles Law is based on a simple idea, when the temperature of a gas goes up its volume expands and the other way around. This connection makes sense once you understand it. Picture a balloon sitting in the sun. As the day heats up the balloon gets bigger. That’s how Charles Law works. Here are the key points,
- Direct Proportionality: The volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature in Kelvin. This means if the temperature goes up, the volume goes up by the same ratio, and if the temperature drops, the volume decreases proportionally.
- Constant Pressure: This law assumes that the pressure of the gas remains constant. If pressure changes, it’s not Charles’s Law that applies, but rather other gas laws like Boyle’s Law.
- Absolute Temperature: Temperatures must be measured in Kelvin for Charles’s Law to apply correctly. Celsius or Fahrenheit temperatures need to be converted to Kelvin to maintain the accuracy of the law.
Grasping these concepts can greatly simplify tackling gas related issues. Its all about recognizing the impact of temperature fluctuations on volume while keeping pressure constant.
Key Equations in Charles’s Law
To apply Charles’s Law effectively, familiarity with its fundamental equations is crucial. Here’s a concise overview of the key formulas.
| Equation | Description |
|---|---|
| V1/T1 = V2/T2 | This is the core equation of Charles’s Law, where V1 and V2 are the initial and final volumes of the gas, and T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures in Kelvin. |
| V = kT | Here, V represents the volume of the gas, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and k is a constant representing the amount of gas and pressure. This equation shows that volume is directly proportional to temperature. |
Imagine you’re tackling a challenge that involves determining the updated volume of a gas as its temperature shifts. To solve this you would apply the initial equation. For instance if a gas starts off with a volume of 2 liters at 300 K and its temperature rises to 600 K you would compute the new volume like this,
V2 = (V1 × T2) / T1
Substitute the values:
V2 = (2 L × 600 K) / 300 K = 4 L
The updated capacity will be 4 liters. This straightforward equation proves useful in a range of situations including scientific research and real world cases such as estimating how balloons will expand at different temperatures.
Practical Examples of Charles’s Law
Charles Law goes beyond being an idea; it plays a role in our everyday lives. I remember my chemistry lab experiment where we witnessed Charles Law in action. We took a balloon and gently warmed it with a hairdryer. As the balloon heated up it swelled showing how temperature influences volume. Here are some more real life scenarios.
- Hot Air Balloons: The principle behind hot air balloons is a beautiful example of Charles’s Law. When the air inside the balloon is heated, its volume increases, causing the balloon to rise. This expansion is what allows the balloon to lift off the ground.
- Weather Balloons: Weather balloons are filled with helium and released into the atmosphere. As they ascend and encounter lower temperatures, they expand due to Charles’s Law. This helps meteorologists gather data on atmospheric conditions at various altitudes.
- Cooking: When you cook food in a sealed container, such as a pressure cooker, the air inside heats up and expands. Although pressure plays a role here, Charles’s Law helps explain why containers can bulge or even burst if not used properly.
These instances illustrate that Charless Law is not merely theoretical but also intricately woven into real life situations. Its intriguing to witness how a scientific concept influences the happenings in our daily lives!
How to Solve Charles’s Law Problems
At first tackling Charles’s Law problems may appear challenging, but with some practice it becomes second nature. I recall facing difficulties with these issues during my school days but consistent effort made a significant impact. Here’s a guide to help you approach Charles’s Law problems, efficiently.
- Identify the Known Values: Start by noting down the initial volume (V1), initial temperature (T1), final temperature (T2), and the final volume (V2) if given. Ensure temperatures are in Kelvin.
- Use the Charles’s Law Formula: Apply the formula V1/T1 = V2/T2. If you need to find V2, rearrange the formula to V2 = (V1 × T2) / T1.
- Plug in the Values: Substitute the known values into the formula. Double-check your units and ensure that temperatures are converted to Kelvin before calculation.
- Calculate and Interpret: Perform the calculations and interpret the results in the context of the problem. For example, if you’re calculating the volume of a gas at a new temperature, ensure the result makes sense.
If you follow these steps you’ll discover that tackling Charles Law challenges becomes a lot simpler. Experiment with situations and before you know it, it will become second nature to you!
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When dealing with Charles’s Law there are some mistakes that tend to happen. This is particularly true for beginners in the subject. I remember making these blunders myself when I first started learning about it which made the process more challenging. Here are some common traps to watch out for and suggestions on how to steer clear of them.
- Ignoring Units: One of the most frequent mistakes is not converting temperatures to Kelvin. Using Celsius or Fahrenheit can lead to incorrect results. Always remember to add 273.15 to your Celsius temperature to convert it to Kelvin.
- Forgetting Constant Pressure: Charles’s Law assumes constant pressure. If pressure changes, you need to use the combined gas law. Always check that the pressure remains unchanged in your problem.
- Misplacing Decimal Points: Simple calculation errors, like misplaced decimal points, can lead to wrong answers. Double-check your arithmetic and ensure calculations are accurate.
- Not Understanding Proportions: Sometimes, students mix up direct proportionality with inverse proportionality. Remember, Charles’s Law is about direct proportionality: as temperature increases, volume increases proportionally.
By paying attention to these errors and approaching each challenge with a careful and systematic mindset you can steer clear of the traps linked, to Charles’s Law. With consistent effort and a focus on precision you’ll grasp this idea before you know it!
Additional Resources for Learning Charles’s Law
Having wrestled with Charles’s Law in the past I can attest to the value of having a variety of resources at your disposal to reinforce your comprehension. While textbooks and lectures serve as foundations sometimes a little extra assistance is needed. Here are some supplementary resources that can make the process of learning about Charles’s Law not only engaging but also enlightening.
- Online Tutorials and Videos: Platforms like Khan Academy and YouTube offer excellent video tutorials. These resources break down complex concepts into digestible parts, often with visual aids that can make the principles clearer. I vividly remember watching a few videos that transformed my grasp of the topic.
- Interactive Simulations: Websites such as PhET Interactive Simulations provide interactive tools where you can experiment with Charles’s Law in a virtual environment. These tools let you manipulate variables and see the results in real time, which is incredibly helpful for visual learners.
- Textbooks and Reference Books: Books like “Chemistry: The Central Science” by Brown, LeMay, and Bursten offer in-depth explanations and practice problems. Often, these textbooks include real-life examples and detailed explanations that can enrich your understanding.
- Online Forums and Study Groups: Engaging with communities on platforms like Reddit or joining study groups can provide you with additional perspectives and problem-solving tips. Sharing and discussing problems with peers can often reveal new insights and solutions.
These materials offer a balanced way to grasp the principles of Charles’s Law. Whether you lean towards engaging tools, informative videos or classic textbooks there’s a resource available that suits your preferred method of learning.
FAQs about Charles’s Law
Grasping Charles’s Law might bring up some inquiries, particularly if you’re just starting out. Drawing from my knowledge and usual questions, here are a few commonly asked ones regarding Charles’s Law.
- What is Charles’s Law? Charles’s Law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when pressure is constant. In simpler terms, if you heat a gas, it expands; if you cool it, it contracts.
- Why do we use Kelvin for temperature in Charles’s Law? The Kelvin scale is used because it starts at absolute zero, where the volume of a gas theoretically reaches zero. This makes it easier to work with direct proportionality in calculations.
- Can Charles’s Law be applied to liquids or solids? No, Charles’s Law specifically applies to gases. The behavior of liquids and solids under temperature changes is governed by different principles.
- What if the pressure of the gas changes? If the pressure changes, Charles’s Law no longer applies directly. Instead, you would need to use the combined gas law or other gas laws that account for changes in pressure as well as temperature.
- How can I remember Charles’s Law? A simple way to remember it is through practical examples, like a balloon expanding when heated. Associating the law with everyday phenomena can make it easier to recall and understand.
These frequently asked questions tackle some of the questions and interests related to Charless Law. If you have inquiries seeking out more information or consulting a well informed friend or teacher can prove beneficial.
Conclusion
Charles’s Law provides an insight into how temperature and volume are connected in gases. Based on my experience grasping this idea can lay the groundwork for grasping more intricate scientific concepts. Whether you’re determining the volume of a gas or witnessing practical uses such as hot air balloons Charles’s Law proves to be both valuable and intellectually rewarding. By utilizing resources steering clear of pitfalls and honing your problem solving skills you can develop a comprehensive understanding of this essential principle. Keep in mind that similar to scientific concepts a sprinkle of curiosity and perseverance can take you far. Enjoy your journey of learning!


