Common Law in Ontario: A Guide to Legal Principles
Common law is a fundamental part of the legal system in Ontario, shaping how laws are interpreted and applied. It is a system based on judicial decisions rather than written statutes. In Ontario, common law helps to fill gaps in legislation, ensuring that justice is served even in complex cases. Understanding common law is essential for anyone navigating the legal landscape in Ontario, whether you’re a lawyer, a student, or just a curious citizen.
History of Common Law in Ontario

The roots of common law in Ontario can be traced back to England. Here’s a brief timeline of its development:
- 1066: The Norman Conquest introduces a system of laws based on royal decrees and local customs.
- 1215: The Magna Carta establishes the principle that no one is above the law.
- 17th Century: The establishment of common law courts in England leads to the formalization of legal precedents.
- 1867: The British North America Act creates the Dominion of Canada, adopting English common law as a foundation.
Over the years, Ontario’s common law has evolved through various judicial rulings, adapting to societal changes and legal needs. The legal principles established in past cases continue to influence current law, ensuring a cohesive legal system.
Key Principles of Common Law
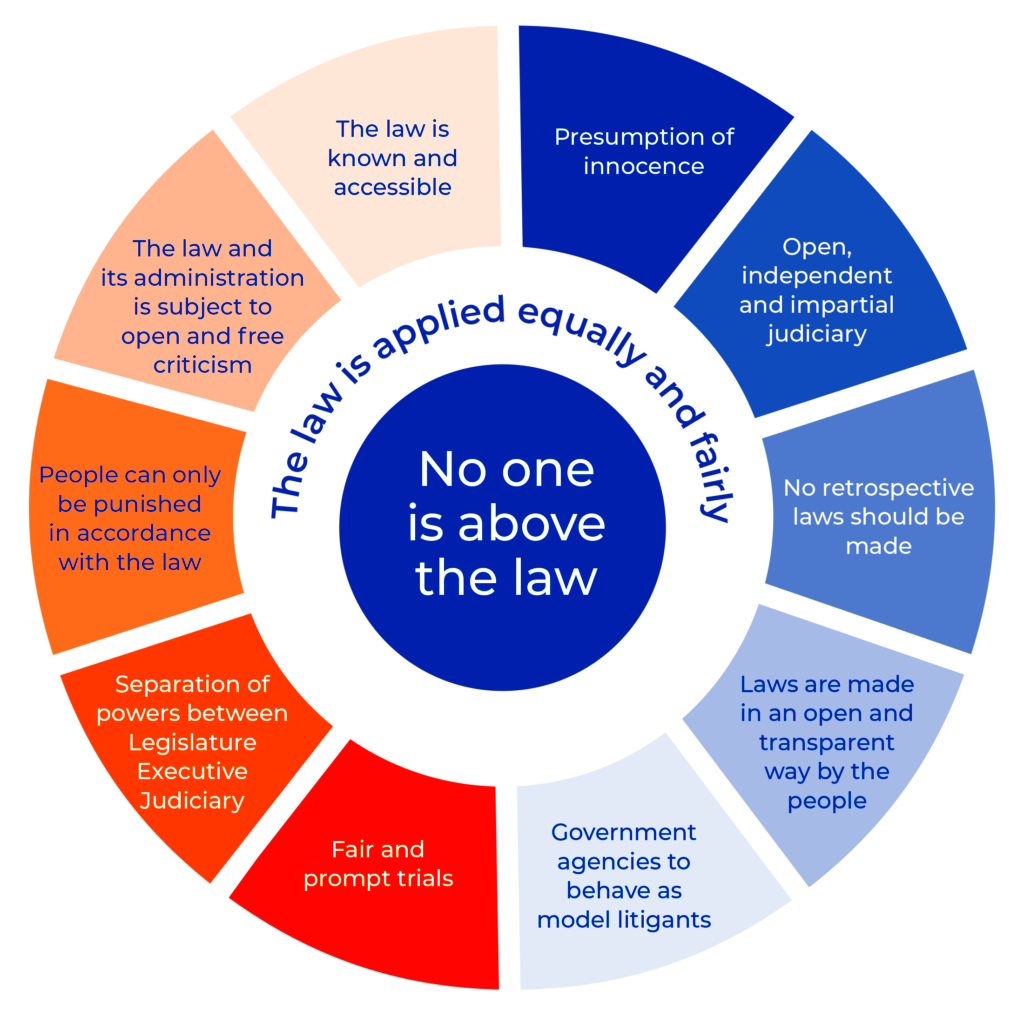
Common law is characterized by several key principles that guide legal interpretations and rulings:
- Precedent: Courts follow the decisions made in previous cases, known as *stare decisis*. This ensures consistency and predictability in the law.
- Judicial Interpretation: Judges play a crucial role in interpreting laws, filling in gaps, and adapting legal principles to new situations.
- Adversarial System: Legal disputes are resolved through an adversarial process where opposing parties present their arguments before a judge.
- Equity: Common law incorporates principles of equity, allowing for fairness and justice when strict application of the law might lead to unjust outcomes.
These principles not only define how the law operates in Ontario but also ensure that the legal system remains fair and adaptable to the needs of its citizens. Understanding these principles is vital for anyone engaging with the legal system.
Differences Between Common Law and Civil Law
Common law and civil law are two major legal systems that operate around the world. While both aim to maintain justice, they differ significantly in their structure and approach. Here’s a quick breakdown of the key differences:
| Aspect | Common Law | Civil Law |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Developed from English law | Based on Roman law |
| Legal Source | Judicial decisions and precedents | Written codes and statutes |
| Role of Judges | Active role in shaping law through rulings | Primarily apply the law as written |
| Legal Proceedings | Adversarial system | Inquisitorial system |
| Flexibility | More adaptable to change | Less flexible, relies on codification |
Understanding these differences is essential for anyone studying law or engaging with legal systems. Each system has its advantages and disadvantages, shaping how justice is delivered in various jurisdictions.
Role of Precedents in Common Law
Precedents play a crucial role in the common law system. They are past judicial decisions that guide judges in deciding current cases. Here’s why they matter:
- Consistency: Following precedents helps ensure that similar cases are treated similarly, promoting fairness.
- Predictability: When people know how courts have ruled in the past, they can better anticipate the outcomes of their cases.
- Evolution of Law: Precedents can evolve over time, allowing the law to adapt to new societal norms and values.
- Judicial Efficiency: By relying on established rulings, courts can save time and resources, leading to quicker resolutions.
However, judges are not bound to follow precedents in every situation. They can choose to distinguish a case based on its unique circumstances or even overturn outdated precedents if necessary. This balance between consistency and adaptability is what makes common law dynamic.
Common Law Courts in Ontario
Ontario’s legal landscape features a variety of common law courts, each serving a specific function. Here’s a look at the primary courts:
- Ontario Superior Court of Justice: This is the trial court for serious criminal cases, civil disputes, and family law matters.
- Ontario Court of Appeal: This court hears appeals from the Superior Court, ensuring that legal errors are corrected.
- Small Claims Court: A more accessible court for resolving minor civil disputes, usually involving claims up to a specified amount.
- Family Court: Part of the Superior Court, it deals specifically with family law issues, such as divorce and child custody.
These courts play a vital role in interpreting and applying common law principles in Ontario. Each court operates under specific rules and procedures, ensuring that justice is delivered effectively and efficiently. Understanding the function of these courts can help individuals navigate the legal system more effectively.
Impact of Statutory Law on Common Law
Statutory law refers to laws that are enacted by legislatures, such as the Ontario Parliament. These laws have a significant impact on common law, often shaping how legal principles are applied. Here’s how statutory law influences common law:
- Codification of Laws: Statutory laws can codify existing common law principles, making them easier to understand and apply. This means that some common law rules are formally written into legislation.
- Overriding Common Law: When a statute is enacted, it can override previous common law decisions. For example, if a law is passed that specifically addresses a legal issue, courts will apply the statute rather than rely on common law precedents.
- Clarification of Ambiguities: Statutory law often provides clarity in areas where common law may be ambiguous. This helps reduce uncertainty and ensures that individuals and businesses understand their rights and obligations.
- Dynamic Relationship: The relationship between statutory law and common law is dynamic. As society evolves, new statutes may be introduced, which can modify or refine common law principles.
Overall, statutory law plays a crucial role in shaping the common law landscape in Ontario, ensuring that the legal system remains relevant and effective in addressing contemporary issues.
Common Law in Family Law Matters
Family law is an area where common law principles play a significant role. In Ontario, many family law issues are addressed through common law, especially in the absence of specific statutory regulations. Here are some key aspects:
- Divorce and Separation: Common law principles help guide decisions regarding the division of assets and responsibilities during divorce or separation.
- Child Custody: Courts rely on established common law precedents to determine custody arrangements that serve the best interests of the child.
- Spousal Support: Common law plays a role in determining the fairness and appropriateness of spousal support payments based on past cases.
- Common Law Relationships: In Ontario, common law relationships—where couples live together without being married—are recognized, and common law principles apply to issues like property division and support obligations.
Family law can be complex, and common law provides a framework that helps ensure fair outcomes for all parties involved. Understanding these principles can be essential for anyone navigating family-related legal matters.
FAQ
What is common law?
Common law is a legal system based on judicial decisions and precedents rather than written statutes. It evolves over time as judges make new rulings.
How does common law differ from statutory law?
Common law is derived from court decisions, while statutory law is created by legislative bodies. Statutory law can override common law if there is a conflict.
What role do judges play in common law?
Judges in common law systems interpret laws, apply precedents, and sometimes create new legal principles through their rulings.
Are common law marriages recognized in Ontario?
Yes, Ontario recognizes common law relationships, and legal principles apply to matters such as property division and support obligations in these cases.
How does common law affect family law cases?
Common law principles guide decisions in family law matters, including divorce, custody, and support, ensuring fairness and consistency in outcomes.
Conclusion
Understanding common law in Ontario is essential for navigating the legal landscape, especially in areas like family law and statutory interactions. Common law, shaped by precedents and judicial interpretations, provides flexibility and consistency in the legal system. While statutory law plays a critical role in codifying and sometimes overriding common law principles, the two systems work together to ensure justice is served. By grasping these concepts, individuals can better understand their rights and obligations, making informed decisions in legal matters. Whether you are involved in a family dispute or seeking clarity on legal principles, familiarity with common law is invaluable.


