Essential Principles of Insurance Law
Insurance law is a vital area of legal practice that governs the relationship between insurers and the insured. It ensures that both parties understand their rights and obligations. This area of law not only covers the formation and enforcement of insurance contracts but also the claims process and any disputes that may arise. By establishing clear rules, insurance law helps to maintain trust and fairness in the insurance industry.
Understanding Different Types of Insurance

Insurance can be categorized into several types, each serving a distinct purpose. Here are the main types:
- Life Insurance: Provides financial support to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death.
- Health Insurance: Covers medical expenses for the insured, including doctor visits and hospital stays.
- Auto Insurance: Protects against financial loss in the event of an accident involving a vehicle.
- Homeowners Insurance: Offers protection for a home and its contents against damage or theft.
- Liability Insurance: Covers legal costs and claims made against an insured party for negligence or harm.
Each type of insurance has specific terms and conditions that policyholders should understand to ensure they have adequate coverage.
Key Principles Governing Insurance Contracts
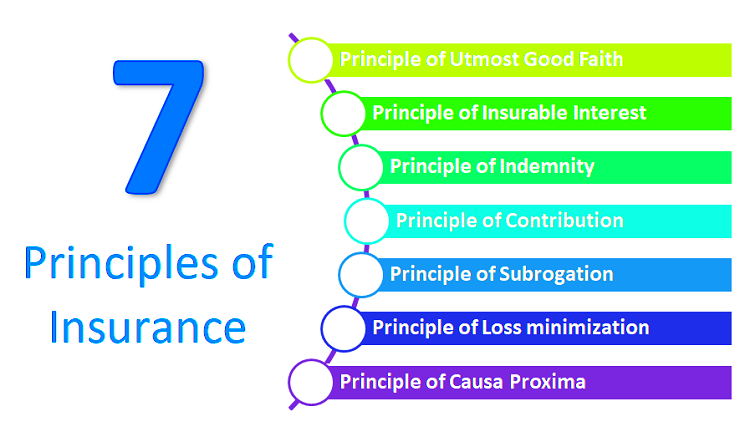
Insurance contracts are based on several fundamental principles that guide their creation and enforcement. Understanding these principles can help policyholders make informed decisions. Here are the key principles:
- Utmost Good Faith (Uberrimae Fidei): Both parties must act honestly and disclose all relevant information. Failure to do so can lead to contract voiding.
- Insurable Interest: The insured must have a legitimate interest in the subject matter of the insurance, meaning they would suffer a financial loss if an insured event occurs.
- Indemnity: This principle ensures that the insured is compensated for losses but does not profit from the insurance. The compensation should reflect the actual loss incurred.
- Subrogation: After paying a claim, the insurer can pursue recovery from third parties responsible for the loss, ensuring the insured does not receive double compensation.
- Proximate Cause: This principle establishes that the insurer is liable only for losses directly caused by an insured event, guiding claim evaluations.
By adhering to these principles, insurance contracts can foster fair treatment for all parties involved.
Duties of the Insured and Insurer
In any insurance contract, both the insured and the insurer have specific duties they must fulfill. Understanding these responsibilities is essential for maintaining a smooth relationship and ensuring claims can be processed efficiently. Let’s take a closer look at these duties:
Duties of the Insured:
- Disclosure of Information: The insured must provide accurate and complete information when applying for insurance. This includes any health issues, previous claims, or other relevant facts.
- Payment of Premiums: It’s crucial for the insured to pay premiums on time to keep the policy active. Failure to pay can result in coverage lapsing.
- Reporting Incidents: In case of an event that might lead to a claim, the insured should report it to the insurer promptly.
- Mitigation of Loss: The insured should take reasonable steps to prevent further loss after an incident occurs.
Duties of the Insurer:
- Clear Communication: The insurer must explain policy terms and conditions in a way that the insured can easily understand.
- Timely Payment of Claims: Once a claim is validated, the insurer should process and pay out claims in a timely manner.
- Fair Claims Handling: Insurers must investigate claims fairly and without bias, ensuring that all valid claims are honored.
By fulfilling these duties, both the insured and the insurer can help create a respectful and productive relationship.
Claims Process and Procedures
The claims process can often seem daunting, but knowing what to expect can make it much easier for policyholders. Here’s a straightforward breakdown of the typical claims process:
- Notification: The insured must inform the insurer about the incident as soon as possible, providing essential details.
- Claim Submission: The insured submits a formal claim, usually including a claim form and supporting documents like photos or police reports.
- Investigation: The insurer will investigate the claim, gathering information and determining the validity of the claim.
- Evaluation: After the investigation, the insurer evaluates the claim based on the policy’s terms and the evidence provided.
- Decision: The insurer will either approve or deny the claim. If approved, the payout amount will be communicated to the insured.
- Payment: Once approved, the insurer processes the payment to the insured or the service provider.
Understanding these steps can help policyholders navigate the claims process more effectively and reduce stress during potentially challenging times.
Dispute Resolution in Insurance Law
Despite best efforts, disputes may arise between the insured and the insurer. It’s important to know how to resolve these conflicts effectively. Here’s an overview of the common methods for dispute resolution in insurance law:
1. Negotiation:
This is often the first step in resolving disputes. Both parties can discuss the issues and try to reach an agreement without any formal process.
2. Mediation:
In mediation, a neutral third party helps both sides communicate and work towards a mutually acceptable resolution. It’s less formal than arbitration or court and can be a quicker, cheaper option.
3. Arbitration:
If negotiation and mediation fail, arbitration might be the next step. In this process, an arbitrator hears both sides and makes a binding decision. This method is usually faster than going to court.
4. Litigation:
If all else fails, the insured may choose to take the matter to court. This is often the most time-consuming and costly option, but it may be necessary in some situations.
By knowing these dispute resolution methods, policyholders can better prepare themselves for any issues that may arise with their insurance claims.
Impact of Regulation on Insurance Practices
Regulations play a crucial role in shaping the insurance industry. They ensure that insurers operate fairly and responsibly while protecting consumers. Understanding these regulations can help policyholders navigate their insurance journeys better. Let’s look at some key impacts of regulation on insurance practices:
- Consumer Protection: Regulations are designed to protect consumers from unfair practices. They require insurers to provide clear information about policies, so consumers can make informed decisions.
- Financial Stability: Regulatory bodies monitor insurance companies to ensure they maintain sufficient reserves. This stability helps guarantee that insurers can pay claims, even during large-scale disasters.
- Rate Approval: In many jurisdictions, insurers must get approval for premium rates before they can be implemented. This oversight helps prevent excessive rate increases.
- Market Conduct: Regulations set standards for how insurers interact with customers, ensuring ethical practices during sales, marketing, and claims handling.
- Solvency Regulation: Insurers are required to maintain certain levels of solvency to operate, which reduces the risk of insolvency and protects policyholders.
By promoting fair practices and consumer protection, regulations contribute to a more stable and trustworthy insurance industry.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding insurance law can be challenging, so here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify common concerns:
1. What should I do if my claim is denied?
If your claim is denied, review the denial letter carefully. It should explain the reasons for the denial. You can appeal the decision by providing additional evidence or clarification to support your claim.
2. How long do I have to file a claim?
Most policies specify a timeframe within which you must file a claim. This can range from a few days to several months after the incident. Always check your policy for specific deadlines.
3. Can I change my insurance policy?
Yes, you can change your insurance policy. Contact your insurer to discuss adjustments to your coverage, premiums, or limits. Be aware that changes may affect your premiums.
4. What if I don’t agree with the insurer’s settlement offer?
If you believe the settlement offer is too low, you can negotiate with the insurer or seek an independent assessment. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as dispute resolution methods.
5. Are all insurance policies regulated?
Yes, most insurance policies are regulated by state or national authorities to ensure they comply with legal standards and consumer protection laws.
Conclusion
Insurance law is an essential aspect of the legal landscape that affects individuals and businesses alike. Understanding the key principles, duties, claims processes, and dispute resolution methods can empower policyholders to navigate their insurance needs more effectively. Regulation plays a vital role in ensuring fair practices and consumer protection within the industry. By staying informed and proactive, you can better protect yourself and your interests when it comes to insurance.


