Indiana Insurance Regulations: What You Need to Know
The primary aim of insurance laws in the state of Indiana is to guarantee that individuals have access to the necessary protection while at the same time, they remain just and responsible in their actions. There is supervision over these regulations by the Indiana Department of Insurance; an agency committed to safeguarding consumers and ensuring compliance by insurance companies with statewide legislations.The major objectives of Indiana’s insurance laws are:Various types of insurance fall under Indiana’s insurance regulations, including auto, health, homeowners’, and business insurances. These regulations are vital for individual and business policyholders to comprehend their rights and responsibilities together with the standards that insurance firms should conform to.Indiana law prescribes particular kinds of insurance for the sake of protecting its residents. Individuals and businesses need to understand these criteria so that they can comply with the law and avoid being fined. Below are some of the main insurance classes mandated in Indiana:The regulation of auto insurance in Indiana ensures that drivers are financially accountable when this happens. These are the key regulations for the state:Thus, it is possible for drivers in Indiana to effectively shield themselves against any kind of legal or monetary penalties if they follow these laws.
- Ensuring that insurance policies are fair and transparent.
- Protecting consumers from fraudulent practices.
- Maintaining a competitive market for insurance providers.
- Guaranteeing that insurance companies are financially stable and able to meet their obligations.
Types of Insurance Required in Indiana
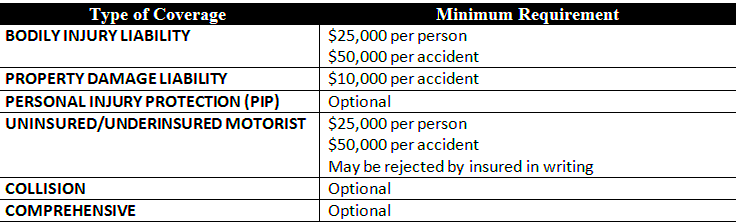
- Auto Insurance: Indiana law requires all drivers to carry liability insurance. This includes:
- Minimum liability coverage of $25,000 for bodily injury per person.
- $50,000 for bodily injury per accident.
- $25,000 for property damage.
- Health Insurance: While Indiana does not mandate health insurance coverage for individuals, the Affordable Care Act requires most people to have health insurance or face a penalty. Many employers provide health insurance as part of their employee benefits.
- Homeowners Insurance: Although not legally required, homeowners insurance is essential for protecting one’s property and belongings. Lenders typically require this insurance for mortgage approval.
- Business Insurance: Depending on the business type, various insurance coverages may be required, including workers’ compensation and liability insurance.
Key Rules for Auto Insurance in Indiana
- Minimum Coverage Requirements: Indiana law mandates that drivers maintain at least the following coverage:
- $25,000 per person for bodily injury.
- $50,000 per accident for bodily injury.
- $25,000 for property damage.
- Proof of Insurance: Drivers must carry proof of insurance at all times and provide it when requested by law enforcement. Failure to provide proof can result in fines and license suspension.
- Uninsured Motorist Coverage: Indiana requires drivers to have uninsured motorist coverage to protect against accidents involving drivers without insurance.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to maintain the required insurance can lead to significant penalties, including fines, vehicle impoundment, and license suspension.
Health Insurance Guidelines in Indiana
Health insurance in Indiana provides critical protection against high medical costs and ensures access to essential healthcare services. While Indiana does not mandate individual health insurance coverage, federal laws under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) influence insurance requirements and coverage options.
Here are the key health insurance guidelines in Indiana:
- Marketplace Insurance: Indiana residents can obtain health insurance through the federal Health Insurance Marketplace (Healthcare.gov). The marketplace offers a range of plans with varying coverage levels and costs, with potential subsidies based on income.
- Essential Health Benefits: Health insurance plans must cover essential health benefits, including:
- Ambulatory patient services
- Emergency services
- Hospitalization
- Maternity and newborn care
- Mental health and substance use disorder services
- Prescription drugs
- Rehabilitative services and devices
- Preventive and wellness services
- Pediatric services
- Pre-existing Conditions: Insurers cannot deny coverage or charge higher premiums due to pre-existing conditions, thanks to the ACA.
- Medicaid and CHIP: Indiana provides health insurance coverage through Medicaid and the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) for eligible low-income individuals and families.
Understanding these guidelines helps individuals make informed decisions about their health insurance coverage and ensures they meet necessary requirements for protection and care.
Homeowners and Renters Insurance Requirements
Homeowners and renters insurance in Indiana safeguard property and personal belongings against damage and loss. Although homeowners insurance is not legally required, it is highly recommended and often required by mortgage lenders. Renters insurance, while not mandatory, provides crucial protection for tenants.
Here are the main aspects of homeowners and renters insurance in Indiana:
- Homeowners Insurance: Homeowners insurance typically includes:
- Dwelling Coverage: Covers damage to the structure of the home due to events like fire, theft, or vandalism.
- Personal Property Coverage: Protects belongings inside the home, such as furniture, electronics, and clothing.
- Liability Coverage: Offers protection if someone is injured on your property or if you cause damage to someone else’s property.
- Additional Living Expenses: Covers costs of temporary housing and living expenses if the home is uninhabitable due to covered damage.
- Renters Insurance: Renters insurance provides similar coverage for tenants, including:
- Personal Property Coverage: Protects tenants’ belongings from risks like fire, theft, and vandalism.
- Liability Coverage: Covers legal costs if a tenant is responsible for injuries or damage to others.
- Additional Living Expenses: Assists with temporary living costs if the rental property becomes uninhabitable.
Both types of insurance offer essential protection and peace of mind, helping individuals manage risks related to property damage and personal liability.
Insurance for Businesses in Indiana
Business insurance in Indiana helps protect companies from financial losses due to various risks, including property damage, liability claims, and employee-related issues. While the specific insurance needs of a business can vary, certain types of coverage are generally essential.
Key types of business insurance in Indiana include:
- General Liability Insurance: Covers legal costs and damages if a business is found liable for injuries or property damage caused by its operations. It typically includes:
- Bodily injury liability
- Property damage liability
- Personal and advertising injury
- Property Insurance: Protects business property, such as buildings, equipment, and inventory, from risks like fire, theft, and vandalism.
- Workers’ Compensation Insurance: Required by Indiana law for businesses with employees, this insurance covers medical expenses and lost wages for employees injured on the job.
- Professional Liability Insurance: Also known as errors and omissions insurance, this coverage protects businesses against claims of negligence or mistakes in professional services.
- Business Interruption Insurance: Provides financial support if a business is forced to close temporarily due to a covered event, such as a natural disaster.
Having the right insurance in place helps businesses in Indiana manage risks, protect their assets, and ensure they can continue operating even in challenging situations.
Insurance fraud constitutes a serious crime which encompasses dishonest maneuvers for the purpose of obtaining undue advantage or financial gain from an insurance policy. On this note, Indiana treats insurance fraud with utmost seriousness through its rigorous legal measures aimed at dealing with any fraudulent acts.Insurance fraud takes on several familiar forms, including:The repercussions of committing an insurance fraud in Indiana are grave and may include:The grasping of such features of insurance scam can be helpful to people and companies so that they do not get involved in unfair acts. It also helps them uphold legal and ethical standards.In Indiana, the processing of an insurance claim is dependent on certain important steps which must be followed. This cannot be taken lightly because proper adherence to the steps is the only way to increase the chances of success as well as provide relevant information.
The below process can assist you to make a successful claim for your insurance in Indiana.Following these steps would help you receive your claims faster and consequently it will lead to you getting your dues as per your insurances.
Understanding Insurance Fraud and Penalties
- False Claims: Submitting a claim for damages or losses that did not actually occur. This can include exaggerating the extent of damage or fabricating incidents.
- Misrepresentation: Providing false information on an insurance application or during the claims process. This might involve underreporting risk factors or omitting relevant details.
- Staged Accidents: Arranging or falsifying an accident to claim insurance money. This includes staging vehicle accidents or injuries to receive compensation.
- Fake Policies: Selling or purchasing non-existent insurance policies or providing counterfeit insurance documents.
- Criminal Charges: Insurance fraud is classified as a felony, which can result in substantial fines and imprisonment.
- Restitution: Offenders may be required to pay restitution to the insurance company for the amount fraudulently claimed.
- Civil Penalties: In addition to criminal penalties, offenders may face civil lawsuits and additional fines.
- Loss of Insurance Coverage: Individuals found guilty of insurance fraud may face difficulties obtaining insurance coverage in the future.
How to File an Insurance Claim in Indiana
- Notify Your Insurance Company: Contact your insurance provider as soon as possible after the incident. Most insurers have a 24/7 claims hotline or online claim submission options.
- Document the Incident: Gather evidence related to the incident, including photographs, police reports, medical records, and any other relevant documents. Detailed documentation supports the claim and helps verify the extent of the damage or loss.
- Complete the Claim Form: Fill out the insurance claim form provided by your insurer. Ensure that all information is accurate and complete. Include details about the incident, the damages or losses incurred, and any involved parties.
- Submit Supporting Documentation: Provide any additional documents required by the insurer, such as receipts, repair estimates, or medical bills. This helps to substantiate the claim and facilitate the processing of your request.
- Follow Up: After submitting your claim, regularly check with your insurance company for updates on the status of your claim. Keep records of all communications and correspondence related to the claim.
- Review the Settlement: Once the insurer processes your claim, review the settlement offer carefully. If you agree with the terms, accept the settlement. If not, discuss the matter with your insurer or consider appealing the decision.