Ohio Child Custody Laws Explained
Understanding child custody laws in Ohio is essential for parents navigating separation or divorce. These laws ensure that the best interests of the child are at the forefront of any custody arrangement. Ohio law provides a framework for determining custody types, visitation rights, and the overall welfare of the child. It’s important for parents to be aware of their rights and responsibilities under these laws to make informed decisions.
Types of Custody in Ohio

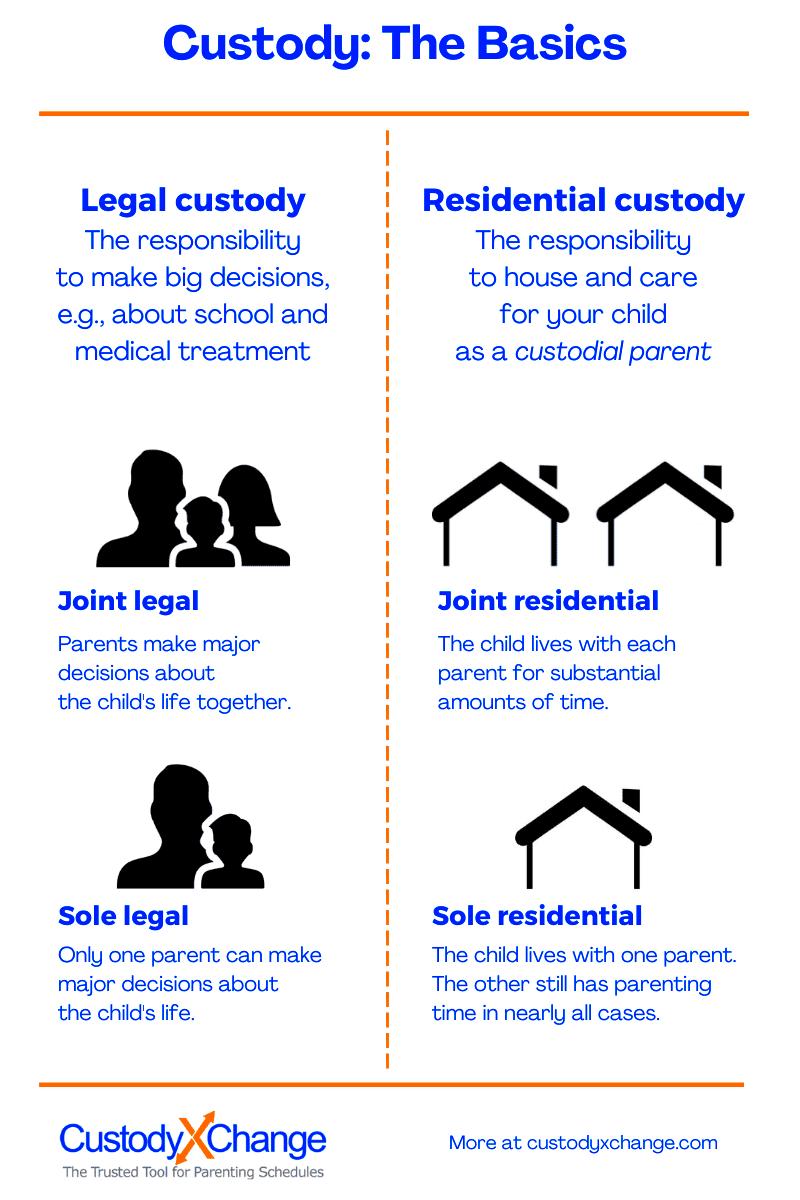
In Ohio, custody is categorized mainly into two types: legal custody and physical custody. Each type serves a specific purpose, and it’s important for parents to understand them.
- Legal Custody: This grants a parent the right to make significant decisions about the child’s life, including education, healthcare, and religious upbringing. Legal custody can be awarded to one parent (sole legal custody) or shared between both parents (joint legal custody).
- Physical Custody: This refers to where the child lives. Similar to legal custody, physical custody can be sole or joint. In joint physical custody, the child spends significant time living with both parents, while sole physical custody means the child primarily resides with one parent.
Custody arrangements can be flexible and may be modified as circumstances change. It’s crucial for parents to prioritize the child’s needs and maintain open communication when making custody decisions.
Factors Influencing Custody Decisions

When courts decide on custody arrangements, they consider various factors to ensure the child’s best interests are met. Here are some of the primary factors:
- Child’s Wishes: Depending on the child’s age and maturity, their preferences may influence custody decisions.
- Parental Involvement: Courts evaluate each parent’s involvement in the child’s life, including attendance at school events, doctor visits, and day-to-day care.
- Stability of Environment: A stable home environment is crucial. Courts look at each parent’s living situation and how it supports the child’s needs.
- Work Schedule: A parent’s job flexibility can affect their ability to care for the child, impacting custody arrangements.
- Health and Safety: The physical and mental health of both parents is assessed, along with any history of abuse or neglect.
- Co-parenting Ability: Courts consider how well parents can communicate and cooperate with each other regarding the child’s upbringing.
By weighing these factors, Ohio courts aim to create custody arrangements that foster a loving and supportive environment for the child.
How to File for Custody in Ohio
Filing for custody in Ohio can seem daunting, but understanding the process can make it easier. Whether you’re a parent seeking custody or looking to modify an existing order, knowing the steps to take is crucial. Here’s a simple breakdown of how to file for custody:
- Determine Your Eligibility: Ensure you have legal standing to file for custody. Typically, this means you are a parent or a legal guardian of the child.
- Gather Necessary Documents: Collect all relevant documents, including birth certificates, proof of income, and any records that demonstrate your relationship with the child.
- Complete the Custody Forms: You can find custody forms at your local court or online through the Ohio Supreme Court’s website. Be thorough when filling them out to avoid delays.
- File Your Forms: Submit your completed forms to the appropriate court in your county. There will be a filing fee, so be prepared for that.
- Serve the Other Parent: Once you file, you must serve the other parent with the custody papers. This can be done through a process server or by certified mail.
- Attend the Court Hearing: Prepare for the hearing by gathering evidence and potentially bringing witnesses. The court will listen to both sides before making a decision.
Understanding these steps will help you navigate the custody filing process smoothly, ensuring that your child’s best interests are always prioritized.
Modification of Custody Orders

Life changes, and so can your custody arrangement. If you believe that a modification is necessary, it’s essential to know how to navigate this process in Ohio. Modifying a custody order requires clear justification, typically revolving around the child’s best interests.
Here are some common reasons for modification:
- Change in Circumstances: This could include a significant change in either parent’s living situation, job, or health that impacts their ability to care for the child.
- Child’s Needs: As children grow, their needs evolve. A change in school, extracurricular activities, or health concerns may warrant a modification.
- Parental Conduct: If one parent displays concerning behavior, such as substance abuse or neglect, this can justify a modification request.
To file for a modification, follow these steps:
- File a Motion: Complete a motion to modify custody and submit it to the court.
- Serve the Other Parent: Just like in the initial custody filing, you must notify the other parent of your intent to modify the order.
- Attend the Hearing: Be prepared to present your case with evidence supporting the need for a change.
Ultimately, the court’s decision will focus on what serves the best interests of the child.
Enforcement of Custody Orders
Once a custody order is in place, it’s vital for both parents to adhere to it. However, situations may arise where one parent fails to comply. Understanding how to enforce custody orders in Ohio can help ensure that your rights—and your child’s rights—are protected.
If you believe the other parent is violating the custody order, here’s what you can do:
- Document Violations: Keep detailed records of any incidents, including dates, times, and descriptions of what occurred. This documentation can be crucial in court.
- Communicate with the Other Parent: Sometimes, issues arise from misunderstandings. Try discussing the situation directly to resolve the conflict before escalating it.
- File a Motion for Contempt: If the violations continue, you can file a motion for contempt with the court. This indicates that the other parent is not following the custody order.
- Attend the Court Hearing: Be prepared to present your evidence and explain how the other parent is not complying with the order.
Courts take custody violations seriously, and they can impose penalties, including altering custody arrangements or enforcing compliance. By knowing your rights and how to enforce them, you can help protect your child’s welfare and maintain a stable environment.
Common Misconceptions About Custody
When it comes to child custody in Ohio, there are plenty of myths that can confuse parents. Understanding the truth behind these misconceptions is vital for making informed decisions about your child’s well-being. Let’s explore some of the most common myths surrounding custody laws.
- Myth 1: Mothers Always Get Custody: While mothers often have a strong case for custody, Ohio law prioritizes the child’s best interests over gender. Courts consider many factors when determining custody, not just the parent’s gender.
- Myth 2: Child’s Preference Is Decisive: While a child’s wishes can influence custody decisions, especially for older children, they are not the sole factor. Courts weigh many aspects, including the child’s safety and stability.
- Myth 3: Custody Agreements Are Set in Stone: Custody arrangements can be modified as circumstances change. If a parent has a valid reason, they can file for a modification at any time.
- Myth 4: Joint Custody Means Equal Time: Joint custody does not necessarily mean equal time with each parent. It refers to shared decision-making rights and responsibilities, which can include varying physical time arrangements.
- Myth 5: You Need a Lawyer to Get Custody: While having legal representation can be beneficial, it is not mandatory. Many parents successfully navigate the custody process on their own.
By debunking these myths, parents can better understand their rights and make choices that truly benefit their children.
Frequently Asked Questions
As parents navigate the complexities of child custody in Ohio, they often have questions. Here are some frequently asked questions that may provide clarity:
- What is the difference between legal custody and physical custody?
Legal custody involves decision-making rights, while physical custody refers to where the child lives. - Can custody arrangements change over time?
Yes, custody arrangements can be modified if there are significant changes in circumstances affecting the child’s welfare. - How does the court determine the child’s best interests?
The court considers factors such as the child’s age, emotional ties to each parent, and each parent’s ability to provide a stable environment. - What should I do if the other parent violates the custody order?
Document the violations and attempt to resolve the issue directly. If necessary, you can file a motion for contempt with the court. - Is mediation required in custody disputes?
Ohio encourages mediation to help parents reach amicable agreements, but it is not always mandatory.
Understanding these FAQs can help parents feel more empowered and informed about their rights and options.
Conclusion on Ohio Child Custody Laws
Navigating child custody laws in Ohio can be complex, but with the right information, parents can make informed decisions that prioritize their child’s best interests. Whether you are filing for custody, modifying an existing order, or seeking enforcement, knowing your rights and the legal framework is essential. Keep in mind that every custody case is unique, and it’s crucial to consider the specific circumstances surrounding your situation.
As you move forward, focus on maintaining open communication and a cooperative relationship with the other parent, as this can significantly benefit your child. If needed, don’t hesitate to seek legal advice to ensure you understand your rights and obligations fully.
By staying informed and proactive, you can create a stable, loving environment for your child, no matter the challenges you face.