Tort Law and Alternatives in Legal Cases and Materials
Tort law is a crucial part of the legal system that deals with civil wrongs. Unlike criminal law, which focuses on punishing offenders, tort law aims to provide relief to individuals harmed by the actions of others. This area of law helps ensure that those who suffer injuries or losses can seek compensation and justice. It’s all about accountability and making sure victims can recover from their damages, whether they are physical, emotional, or financial.
Types of Torts

Tort law is divided into several categories, each addressing different types of wrongful acts. Here are the primary types of torts:
- Intentional Torts: These occur when a person deliberately causes harm to another. Examples include assault, battery, and defamation.
- Negligence: This is the most common type of tort, happening when someone fails to act with reasonable care, resulting in harm to another. For example, a car accident caused by distracted driving.
- Strict Liability: In these cases, a person can be held liable for harm without proof of negligence or intent. This often applies to defective products or dangerous activities.
Elements of a Tort Claim
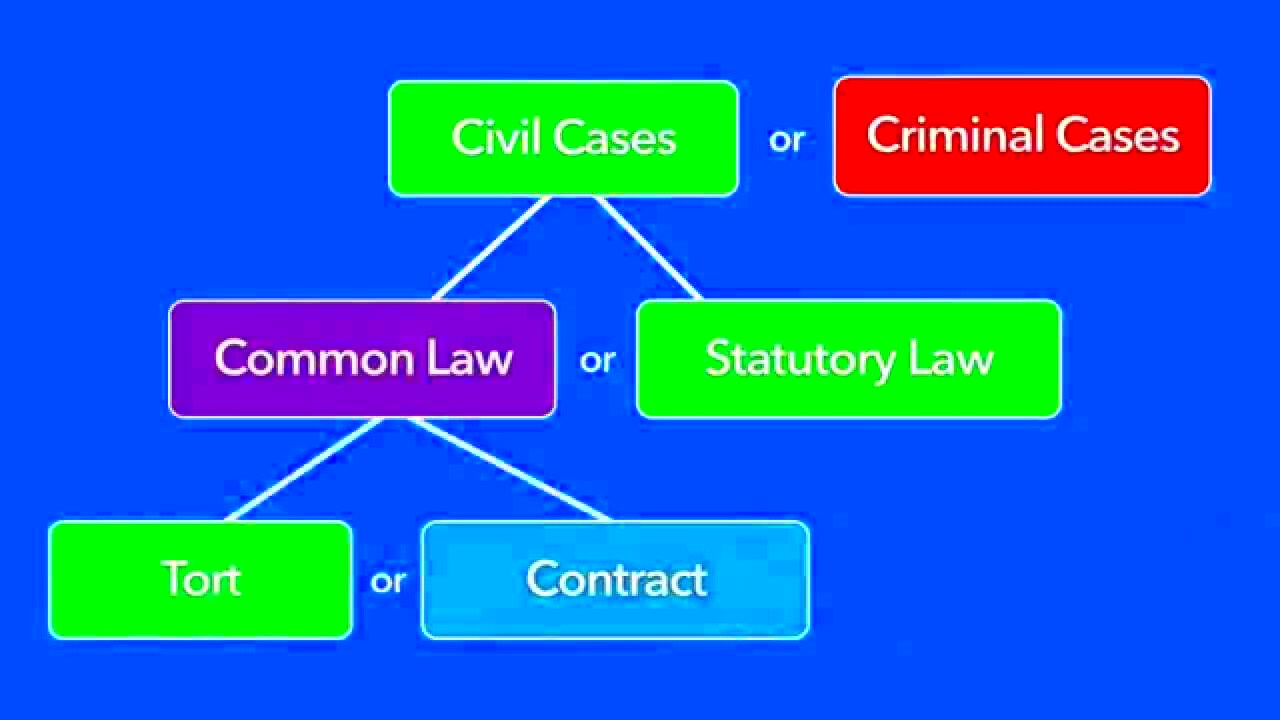
To successfully prove a tort claim, certain elements must be established. Understanding these elements can help clarify how tort cases work:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Duty | The defendant had a legal obligation to act in a certain way toward the plaintiff. |
| Breach of Duty | The defendant failed to meet that obligation, either through action or inaction. |
| Causation | The breach of duty directly caused harm to the plaintiff. This includes both actual cause and proximate cause. |
| Damages | The plaintiff suffered actual damages, which can be physical injuries, emotional distress, or financial losses. |
Understanding these elements is essential for anyone considering pursuing a tort claim, as each must be proven for the case to succeed.
Common Defenses in Tort Cases

In tort law, defendants often use various defenses to challenge the claims against them. Understanding these defenses can help both plaintiffs and defendants navigate the legal landscape. Here are some of the most common defenses used in tort cases:
- Contributory Negligence: This defense argues that the plaintiff’s own negligence contributed to their injury. If proven, it can reduce or eliminate the defendant’s liability.
- Comparative Negligence: Similar to contributory negligence, this defense acknowledges that both parties may share some fault. Damages are then awarded based on the percentage of fault assigned to each party.
- Assumption of Risk: If the plaintiff voluntarily engaged in an activity that carried known risks, the defendant may claim that the plaintiff assumed the risk and should not be compensated.
- Consent: In certain situations, if a plaintiff consented to the defendant’s actions (like in contact sports), this can be used as a defense.
- Self-Defense: If the defendant can prove they acted in self-defense, it can absolve them of liability in cases of intentional torts, such as battery.
Alternatives to Tort Law
While tort law provides a framework for resolving civil disputes, there are alternatives that might be more suitable for certain situations. These alternatives can offer quicker and sometimes less expensive resolutions:
- Negotiation: This informal process involves the parties discussing their issues directly to reach a mutually acceptable agreement without legal intervention.
- Mediation: In this process, a neutral third party helps facilitate discussions between the disputing parties to find common ground and resolve the issue amicably.
- Arbitration: This is a more formal alternative where a neutral third party makes a binding decision after hearing both sides. It’s less formal than court but more structured than mediation.
- Contractual Agreements: Sometimes, parties can include clauses in contracts that specify how disputes will be handled, which can help avoid tort claims altogether.
Benefits of Tort Law
Tort law plays an essential role in promoting justice and accountability. Here are some key benefits of tort law that impact individuals and society:
- Compensation for Victims: Tort law allows victims to receive financial compensation for injuries or losses they have suffered, helping them recover and move forward.
- Deterrence of Wrongful Conduct: By holding individuals and organizations accountable for their actions, tort law discourages negligent or harmful behavior, promoting safer practices.
- Encouragement of Responsible Behavior: Tort law encourages people and businesses to act responsibly, knowing they could face legal consequences for harmful actions.
- Access to Justice: It provides a legal avenue for individuals to seek redress, helping balance power between ordinary people and larger entities.
Overall, tort law serves as a vital mechanism for ensuring fairness and accountability in society.
Challenges in Tort Law
Tort law, while crucial for justice, faces several challenges that can complicate legal proceedings. Understanding these challenges is important for anyone involved in a tort case, whether as a plaintiff or defendant. Here are some of the significant challenges:
- Proving Liability: One of the biggest hurdles is establishing who is at fault. In cases of negligence, plaintiffs must prove that the defendant had a duty, breached that duty, and caused damages.
- Complexity of Cases: Tort cases can involve intricate details, including multiple parties and layers of negligence. This complexity can lead to lengthy and costly legal battles.
- Insurance Issues: Insurance companies often play a significant role in tort cases. Their involvement can complicate negotiations and settlements, as they may try to minimize payouts.
- Limitations on Damages: Some jurisdictions have caps on the amount of damages a plaintiff can recover, which can limit the financial relief available for serious injuries.
- Time Constraints: Many tort cases are subject to statutes of limitations, which can limit the time a plaintiff has to file a claim. This urgency can pressure individuals into making hasty decisions.
Conclusion
Tort law serves as an essential framework for addressing civil wrongs and ensuring accountability. While it provides valuable protections for victims, it also comes with challenges that can complicate legal processes. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating the legal landscape effectively. Whether you’re considering a tort claim or facing one, being informed about the potential hurdles and available alternatives can help you make better decisions. Ultimately, tort law aims to balance justice and responsibility, making our society safer and more equitable for everyone.
FAQ
Here are some frequently asked questions about tort law that may help clarify common concerns:
- What is a tort? A tort is a civil wrong that causes harm or loss to another person, leading to legal liability for the responsible party.
- How do I know if I have a tort case? If you’ve suffered injury or loss due to someone else’s actions or negligence, it’s wise to consult with a legal expert to assess your situation.
- What types of damages can I recover in a tort case? Victims can typically seek compensatory damages for medical expenses, lost wages, pain and suffering, and property damage.
- How long do I have to file a tort claim? Statutes of limitations vary by jurisdiction, so it’s essential to act quickly and consult a legal professional to understand your specific timeline.
- Can I settle a tort claim without going to court? Yes, many tort claims are settled out of court through negotiation or mediation, often resulting in quicker and less expensive resolutions.


