Worksheet for Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law Explained
Boyle’s Law is a fundamental principle in physics and chemistry that describes the relationship between the pressure and volume of a gas. It states that if the temperature of a gas is kept constant, the pressure of the gas is inversely proportional to its volume. This means that when the volume increases, the pressure decreases, and vice versa. The law is named after Robert Boyle, who formulated it in the 17th century.
Mathematically, Boyle’s Law can be expressed as:
P1 × V1 = P2 × V2
Where:
- P1 = initial pressure
- V1 = initial volume
- P2 = final pressure
- V2 = final volume
This relationship can be observed in various everyday scenarios, such as when you squeeze a balloon. As you apply pressure, the volume of the balloon decreases while the pressure inside increases. Understanding Boyle’s Law is essential for applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering.
Understanding Charles’ Law

Charles’ Law describes how gases tend to expand when heated. It states that if the pressure remains constant, the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature in Kelvin. This law is named after Jacques Charles, a French scientist who studied the behavior of gases in the late 18th century.
The mathematical representation of Charles’ Law is:
V1 / T1 = V2 / T2
Where:
- V1 = initial volume
- T1 = initial temperature (in Kelvin)
- V2 = final volume
- T2 = final temperature (in Kelvin)
To put it simply, as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases if the pressure is held constant. A practical example of this can be seen when heating air inside a balloon. As the air warms up, the balloon expands. This law is crucial in various applications, such as hot air balloons and understanding weather patterns.
Key Differences Between Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law
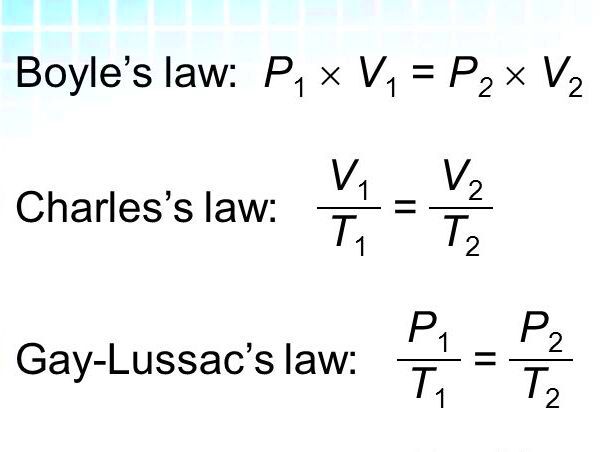
While both Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law deal with the behavior of gases, they highlight different aspects of gas behavior. Here are some key differences:
| Aspect | Boyle’s Law | Charles’ Law |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship | Pressure is inversely proportional to volume | Volume is directly proportional to temperature |
| Constant Variable | Temperature is constant | Pressure is constant |
| Formula | P1 × V1 = P2 × V2 | V1 / T1 = V2 / T2 |
| Real-Life Example | Compressing a balloon | Heating air in a balloon |
Understanding these differences helps clarify the unique principles governing gas behavior and their practical applications in science and everyday life.
Real-Life Applications of Boyle’s Law

Boyle’s Law has several real-life applications that highlight its importance in understanding gas behavior. This law explains many phenomena we encounter daily, making it crucial for various fields, including medicine, engineering, and aviation.
Here are some practical applications:
- Syringes: When you pull back the plunger of a syringe, the volume inside the syringe increases, causing the pressure to drop. This drop allows liquid to flow into the syringe.
- Breathing: When we inhale, our diaphragm moves down, increasing the volume of our chest cavity and decreasing pressure, allowing air to flow into our lungs.
- Vacuum Packaging: When food is vacuum-sealed, the air is removed from the package, decreasing pressure and preventing bacterial growth by creating an oxygen-free environment.
- Scuba Diving: Boyle’s Law is crucial for divers, as pressure increases with depth. Understanding how gas volume changes helps prevent decompression sickness.
These applications demonstrate how Boyle’s Law plays a vital role in everyday life, highlighting its relevance across various fields and practices.
Real-Life Applications of Charles’ Law
Charles’ Law also has significant real-life applications, especially in fields that involve gas behavior under temperature changes. This law helps us understand how gases expand when heated, impacting various technologies and natural processes.
Here are some common applications:
- Hot Air Balloons: As the air inside a hot air balloon is heated, it expands, causing the balloon to rise. The relationship between temperature and volume is crucial for flight.
- Weather Balloons: Meteorologists use weather balloons to measure atmospheric conditions. As the balloon ascends and temperature changes, the volume increases, allowing for accurate readings.
- Automobile Engines: In engines, the combustion of fuel heats the gases, causing them to expand. Understanding this expansion helps improve engine efficiency and performance.
- Thermometers: Many thermometers use liquids that expand and contract with temperature changes. This behavior is based on Charles’ Law, allowing for accurate temperature readings.
These applications show how Charles’ Law is essential in various fields, providing insights into everyday phenomena and technologies.
Common Misconceptions About the Laws
Despite the importance of Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law, there are several common misconceptions that can lead to misunderstandings about gas behavior. Clearing up these misconceptions is essential for a better grasp of these laws.
Here are some prevalent misconceptions:
- Boyle’s Law only applies to ideal gases: While Boyle’s Law is most accurate for ideal gases, it also applies to real gases under certain conditions, especially at low pressures and high temperatures.
- Charles’ Law means gases always expand: While Charles’ Law states that gases expand when heated, it only applies if pressure remains constant. If pressure increases, the gas may not expand.
- Both laws are interchangeable: Boyle’s Law focuses on pressure and volume relationships, while Charles’ Law emphasizes volume and temperature. They govern different aspects of gas behavior.
- Temperature in Charles’ Law can be in Celsius: In Charles’ Law, temperature must be in Kelvin for accurate calculations. Using Celsius can lead to incorrect results.
By understanding these misconceptions, we can better appreciate the true nature of Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law and their applications in our lives.
FAQs About Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law
Understanding Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law can sometimes raise questions, especially for those new to these concepts. Here are some frequently asked questions that may help clarify these important gas laws.
- What is Boyle’s Law in simple terms?
Boyle’s Law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely related to its volume when the temperature is held constant. This means that as the volume increases, the pressure decreases, and vice versa. - What is Charles’ Law in simple terms?
Charles’ Law explains that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature when the pressure is constant. In simpler terms, heating a gas causes it to expand. - Can Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law be used together?
Yes, these laws can be used together when dealing with a gas under varying conditions of pressure, volume, and temperature. The combined gas law incorporates all three variables. - What happens to gas volume when the temperature rises?
According to Charles’ Law, if the pressure is constant, the volume of the gas increases as the temperature rises. - How are these laws applied in the real world?
Boyle’s Law is used in syringes and breathing mechanisms, while Charles’ Law is applied in hot air balloons and weather forecasting. - Do these laws apply to all gases?
While both laws apply most accurately to ideal gases, they can also be applied to real gases under certain conditions, particularly at low pressures and high temperatures.
Conclusion on Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law
Boyle’s Law and Charles’ Law are fundamental principles that provide a deep understanding of gas behavior in various situations. They help explain everyday phenomena and are essential in fields like medicine, engineering, and environmental science. By grasping these concepts, we can better appreciate the science behind many of the technologies and processes we encounter daily.


